1359 Security and Privacy Overview
1359.1 Introduction
IoT security is fundamentally about protecting systems that directly interact with the physical world, making security failures potentially life-threatening rather than merely inconvenient. This comprehensive overview has been split into focused chapters for easier learning.
1359.2 Chapter Structure
This security overview is organized into six focused chapters:
1359.2.1 1. Security and Privacy Foundations
Time: ~45 min | Level: Beginner
Learn the essential concepts: - Why security matters for IoT (real-world incidents: Mirai, Jeep hack, hospital ransomware) - CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability - Security vs Privacy: Understanding the distinction - Why traditional IT security doesn’t work for IoT - Executive summary with ROI analysis
Key Takeaway: Security must be designed in from the start because IoT devices often cannot be patched and compromises can cascade to cause real-world harm.
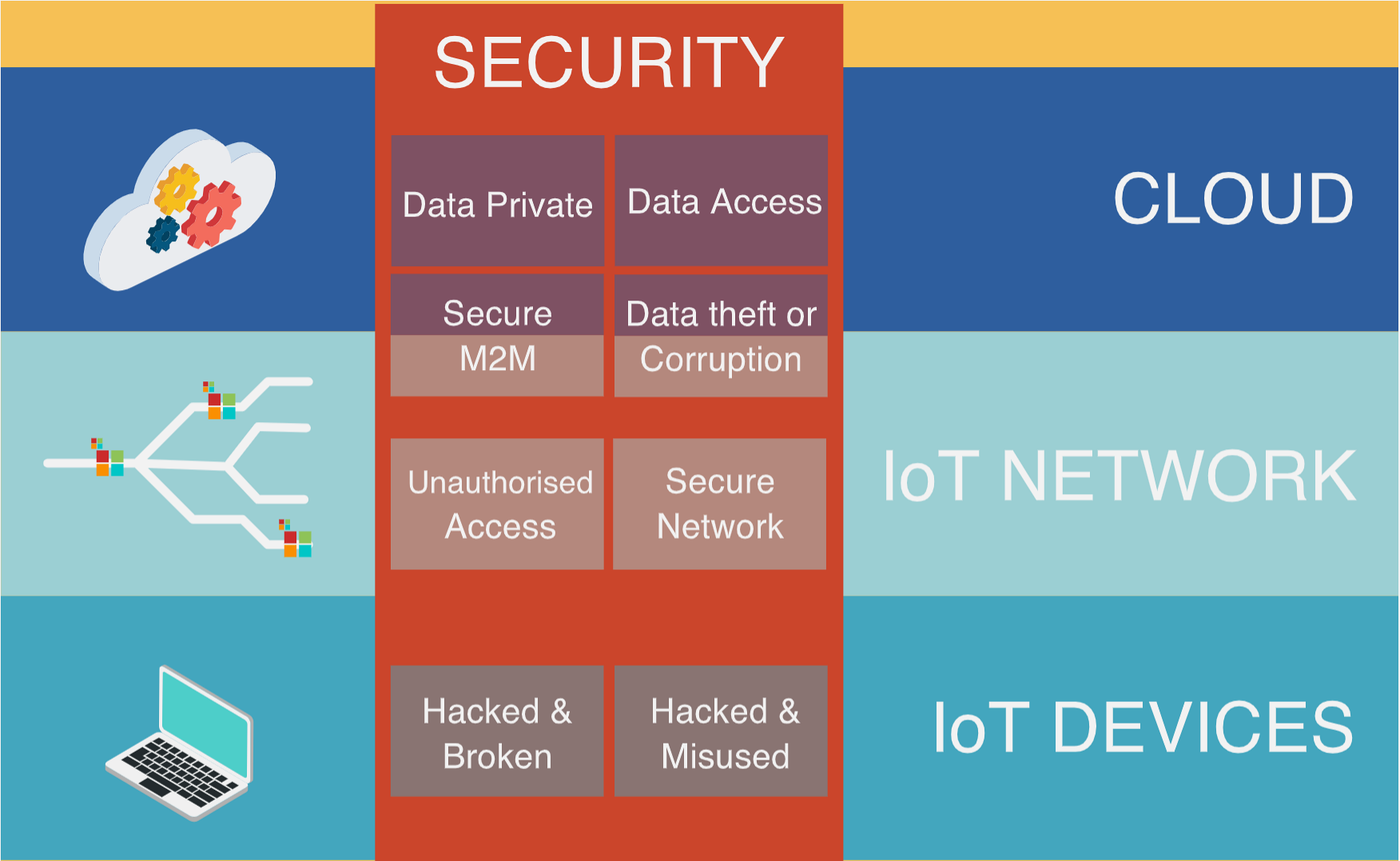
1359.2.2 2. IoT Security Architecture and Attack Surfaces
Time: ~35 min | Level: Intermediate
Understand layered security: - Three-layer IoT architecture (device, network, cloud) - Common attack surfaces and vulnerability points - Defense-in-depth strategies - Attack trees and security maturity models - Code examples for each layer
Key Takeaway: IoT security requires protection at every layer—a single compromised layer can expose the entire system.
1359.2.3 3. IoT Security Frameworks and Standards
Time: ~30 min | Level: Intermediate
Navigate industry standards: - OWASP IoT Top 10 vulnerabilities - NIST 8259 cybersecurity framework - ETSI EN 303 645 baseline requirements - Standards selection framework - Compliance requirements (GDPR, CCPA, PSTI)
Key Takeaway: Following established frameworks prevents reinventing security and ensures regulatory compliance.
1359.2.4 4. Security-by-Design Principles
Time: ~35 min | Level: Intermediate
Apply security from inception: - Security-by-design principles - Common security misconceptions - Minimum viable security requirements - Security vs usability tradeoffs - Real-world implementation patterns
Key Takeaway: Security added after development is expensive and ineffective—build it in from the architecture phase.
1359.2.5 5. IoT Security Case Studies
Time: ~35 min | Level: Intermediate
Learn from real attacks: - Mirai Botnet (2016): How 300,000+ devices were compromised with default passwords - Critical Security Failures: OWASP violations that enabled attacks - Successful Implementations: Smart grid security done right - Regulatory Response: California SB-327, UK PSTI Act - Lessons Learned: Best practices from $3.86M breaches
Key Takeaway: Most IoT breaches exploit basic security failures that are trivial to prevent with proper design.
1359.2.6 6. IoT Security Practice and Assessment
Time: ~2.5 hours | Level: Advanced
This practice section is organized into three focused sub-chapters:
1359.2.6.1 6a. Security Practice Labs
Time: ~60 min
Hands-on security assessment labs:
- IoT device security audit checklists (physical, network, authentication, firmware, privacy)
- Network segmentation for IoT devices (guest network and VLAN configuration)
- HTTPS certificate verification using OpenSSL and browser tools
1359.2.6.2 6b. Exam Preparation Guide
Time: ~45 min
Study materials and practice problems:
- Key concepts to master (CIA triad, OWASP Top 10, defense-in-depth)
- Memory aids and mnemonics for exam recall
- Practice problems with detailed solutions
- Time management strategies for different question types
1359.2.6.3 6c. Advanced Security Concepts
Time: ~50 min
Deep technical knowledge:
- Cryptographic strength and brute-force analysis
- Secure boot chain of trust implementation
- TLS 1.3 vs DTLS performance comparison
- STRIDE threat modeling methodology
- Side-channel attacks and mitigations
Key Takeaway: Security knowledge becomes valuable only through practical application and assessment.
1359.3 Learning Path Recommendations
1359.3.1 For Beginners
Start here and progress through all chapters in order:
- Foundations (understand CIA triad)
- Architecture (see where security applies)
- Frameworks (learn industry standards)
- Design Principles (apply to projects)
- Case Studies (learn from failures)
- Practice Labs (hands-on device audits)
- Exam Preparation (test your knowledge)
Time: ~5 hours total
1359.3.2 For Professionals
If you have IT security background:
- Foundations (focus on “Why Traditional IT Security Doesn’t Work”)
- Architecture (IoT-specific attack surfaces)
- Frameworks (skip if familiar with OWASP)
- Design Principles (IoT-specific tradeoffs)
- Case Studies (Mirai deep dive)
- Advanced Concepts (TLS, secure boot, STRIDE)
- Practice Labs (network segmentation, certificate verification)
Time: ~3 hours (skip familiar content)
1359.3.3 For Executives
Focus on business impact:
- Foundations → Executive Summary section
- Case Studies → Financial impact analysis
- Frameworks → Compliance requirements table
- Design Principles → Investment priorities
Time: ~30 minutes
1359.4 Prerequisites
Basic understanding helpful but not required: - Networking Fundamentals: IP addresses, ports, protocols - IoT Overview: IoT system components and architecture
1359.5 Cross-Hub Connections
Interactive Learning: - Quizzes Hub: 760+ knowledge checks including CIA triad and OWASP Top 10 - Simulations Hub: Security monitoring and encryption demonstrations - Videos Hub: Expert explanations of Mirai and security incidents
Knowledge Management: - Knowledge Gaps Hub: Address misconceptions (e.g., “Default passwords are safe if changed monthly”) - Knowledge Map: Visualize connections between security, protocols, and architectures
1359.6 What You’ll Learn
By completing all chapters and sub-chapters, you’ll be able to:
- Explain why security and privacy are critical for IoT systems
- Apply the CIA triad to IoT security design decisions
- Identify attack surfaces at device, network, and cloud layers
- Navigate OWASP, NIST, and ETSI security frameworks
- Implement security-by-design principles from project start
- Analyze real-world security breaches and extract lessons
- Conduct security audits using industry-standard checklists
- Configure network segmentation for IoT device isolation
- Verify HTTPS/TLS certificates using command-line tools
- Apply STRIDE threat modeling to IoT systems
- Understand cryptographic strength and secure boot chains
1359.8 Get Started
Begin your IoT security journey:
Total Learning Time: 5-6 hours | Difficulty: Beginner to Advanced | Hands-On Labs: 3 | Practice Problems: 4
