%% fig-alt: "Side-by-side comparison of M2M and IoT characteristics showing key differences: M2M uses point-to-point communication while IoT uses cloud-centric many-to-many; M2M has proprietary protocols while IoT standardizes on IP; M2M focuses on single vertical solutions while IoT enables horizontal platforms; M2M scales to thousands while IoT scales to billions; M2M is device-focused while IoT is data and service focused"
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': {'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#E67E22', 'secondaryColor': '#16A085', 'tertiaryColor': '#E67E22', 'fontSize': '11px'}}}%%
graph TB
subgraph M2M["M2M (Machine-to-Machine)"]
M_COMM["Communication:<br/>Point-to-Point<br/>Device ↔ Server"]
M_PROTO["Protocols:<br/>Proprietary<br/>Modbus, BACnet"]
M_ARCH["Architecture:<br/>Vertical Silos<br/>Single vendor"]
M_SCALE["Scale:<br/>1,000s devices<br/>per deployment"]
M_FOCUS["Focus:<br/>Device control<br/>& monitoring"]
end
subgraph IOT["IoT (Internet of Things)"]
I_COMM["Communication:<br/>Many-to-Many<br/>Via cloud"]
I_PROTO["Protocols:<br/>IP-based Standards<br/>MQTT, CoAP, HTTP"]
I_ARCH["Architecture:<br/>Horizontal Platforms<br/>Multi-vendor"]
I_SCALE["Scale:<br/>Billions devices<br/>globally"]
I_FOCUS["Focus:<br/>Data analytics<br/>& AI services"]
end
M_COMM -.->|"evolved to"| I_COMM
M_PROTO -.->|"standardized to"| I_PROTO
M_ARCH -.->|"opened to"| I_ARCH
M_SCALE -.->|"scaled to"| I_SCALE
M_FOCUS -.->|"shifted to"| I_FOCUS
style M2M fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style IOT fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style M_COMM fill:#7F8C8D,color:#fff
style M_PROTO fill:#7F8C8D,color:#fff
style M_ARCH fill:#7F8C8D,color:#fff
style M_SCALE fill:#7F8C8D,color:#fff
style M_FOCUS fill:#7F8C8D,color:#fff
style I_COMM fill:#16A085,color:#fff
style I_PROTO fill:#16A085,color:#fff
style I_ARCH fill:#16A085,color:#fff
style I_SCALE fill:#16A085,color:#fff
style I_FOCUS fill:#16A085,color:#fff
466 M2M vs IoT: Evolution and Comparison
466.1 Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Compare M2M and IoT: Distinguish between M2M communication and broader IoT ecosystems
- Trace M2M Evolution: Understand how M2M evolved into modern IoT architectures
- Identify Key Differences: Recognize scope, protocol, and scalability distinctions
- Apply M2M Patterns: Choose appropriate patterns for closed vs open systems
466.2 Prerequisites
Before diving into this chapter, you should be familiar with:
- M2M Communication Overview: Introduction to machine-to-machine concepts and autonomous device communication
- Networking Basics for IoT: Understanding network protocols, addressing, and communication patterns
466.3 Introduction
Think of M2M as the grandparent of IoT. M2M started in the 1990s with vending machines calling headquarters to report they were empty. IoT is the grandchild that grew up with smartphones, cloud computing, and AI.
Quick comparison: - M2M: Vending machine → Phone line → Company server (closed system) - IoT: Smart light → Wi-Fi → Cloud → Your phone app → Alexa → Your friend’s app (open ecosystem)
Both involve machines talking to each other, but IoT added internet connectivity, cloud platforms, and cross-device interoperability.
While M2M and IoT share similarities, they represent different evolutionary stages of connected devices. Understanding this evolution helps architects choose appropriate patterns for different applications.
466.4 M2M to IoT Evolution
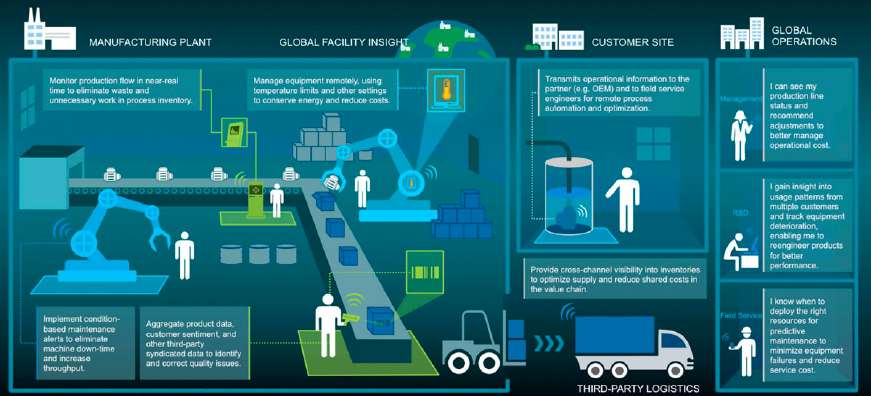
Source: Stanford University IoT Course - Industrial M2M architecture demonstrating autonomous machine-to-machine communication across manufacturing, logistics, and global operations
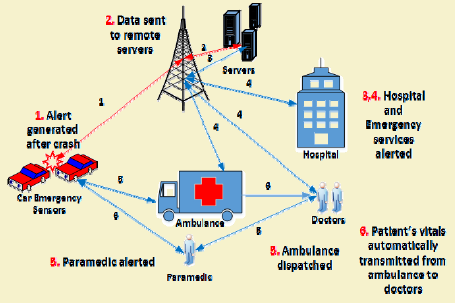
466.5 Key Differences
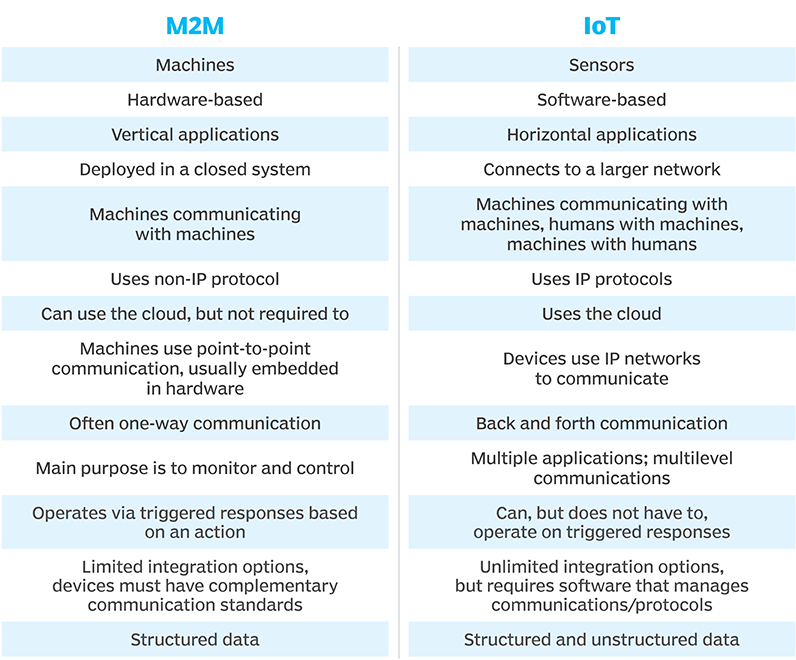
466.5.1 Comparison Table
| Aspect | M2M | IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Device-to-device | Device-to-cloud-to-device |
| Communication | Point-to-point or point-to-server | Many-to-many via internet |
| Protocols | Proprietary (often) | Standardized (MQTT, CoAP, HTTP) |
| Data | Limited processing | Big data analytics, AI/ML |
| Integration | Vertical silos | Horizontal platforms |
| Scalability | Hundreds to thousands | Millions to billions |
| Examples | SCADA, Industrial HMI | Smart cities, Consumer IoT |
M2M Example: Factory machine reports status to local control system via proprietary protocol.
IoT Example: Smart home devices (lights, thermostats, cameras) communicate via cloud platform accessible globally.
466.6 When to Choose M2M Patterns
In one sentence: M2M patterns are optimal for closed, deterministic systems requiring reliable automation; IoT patterns are better for open ecosystems needing interoperability and cloud analytics.
Remember this rule: M2M is point-to-point with domain-specific protocols; IoT adds cloud connectivity, standardized protocols, and cross-domain integration. Choose M2M patterns when you need reliable, deterministic automation in a closed system.
466.6.1 Choose M2M When:
- Closed System: No need for external integrations
- Deterministic Requirements: Predictable, real-time response needed
- Legacy Integration: Working with existing industrial protocols
- Local Control: Processing and decisions stay on-premises
- Security Through Isolation: Air-gapped networks preferred
466.6.2 Choose IoT When:
- Cloud Analytics: Need big data processing and AI/ML
- Remote Access: Users need global access via apps
- Multi-Vendor: Devices from different manufacturers must interoperate
- Ecosystem: Third-party integrations and developer platforms
- Consumer-Facing: End-users interact with devices
466.7 Knowledge Check
466.8 Summary
This chapter examined the evolution from M2M to IoT:
Key Takeaways:
- Historical Context: M2M preceded IoT, establishing patterns for automated data collection
- Architectural Differences: M2M is point-to-point/vertical silos; IoT is cloud-centric/horizontal platforms
- Protocol Evolution: Proprietary protocols gave way to IP-based standards (MQTT, CoAP)
- Scale Transformation: From thousands to billions of devices
- Focus Shift: From device control to data analytics and AI services
Understanding this evolution helps architects choose appropriate patterns: M2M for closed, deterministic systems; IoT for open, cloud-connected ecosystems.
466.9 What’s Next?
Building on the M2M vs IoT comparison, the next chapter explores specific M2M applications and the different node types used across industries.
Continue to M2M Applications and Node Types →
- M2M Communication Overview - Introduction and key concepts
- M2M Applications and Node Types - Industry applications
- M2M Platforms and Networks - Service platforms and network architectures
- Cellular IoT Fundamentals - Cellular M2M networks
