%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#E67E22', 'secondaryColor': '#16A085', 'tertiaryColor': '#E8F6F3'}}}%%
quadrantChart
title Bandwidth vs Coverage Trade-off
x-axis Low Coverage --> High Coverage
y-axis Low Bandwidth --> High Bandwidth
quadrant-1 High BW / High Coverage
quadrant-2 High BW / Low Coverage
quadrant-3 Low BW / Low Coverage
quadrant-4 Low BW / High Coverage
5G: [0.85, 0.9]
Wi-Fi: [0.25, 0.85]
Ethernet: [0.15, 0.95]
Bluetooth: [0.1, 0.5]
Zigbee: [0.2, 0.35]
LoRaWAN: [0.75, 0.15]
Sigfox: [0.85, 0.05]
NB-IoT: [0.7, 0.25]
800 Network Classification: PAN, LAN, and WAN for IoT
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Map IoT protocols to network classifications (PAN, LAN, WAN)
- Understand bandwidth and coverage trade-offs for different protocols
- Design IoT network topologies using appropriate protocol combinations
- Select the right network type based on deployment requirements
- Understand common terminology used in IoT networking
800.1 Prerequisites
Before diving into this chapter, you should be familiar with:
- Network Access and Physical Layer Overview: Understanding physical and network access layers
- Low-Power Networks: 802.15.4, LPWAN, and Cellular: Understanding available protocol options
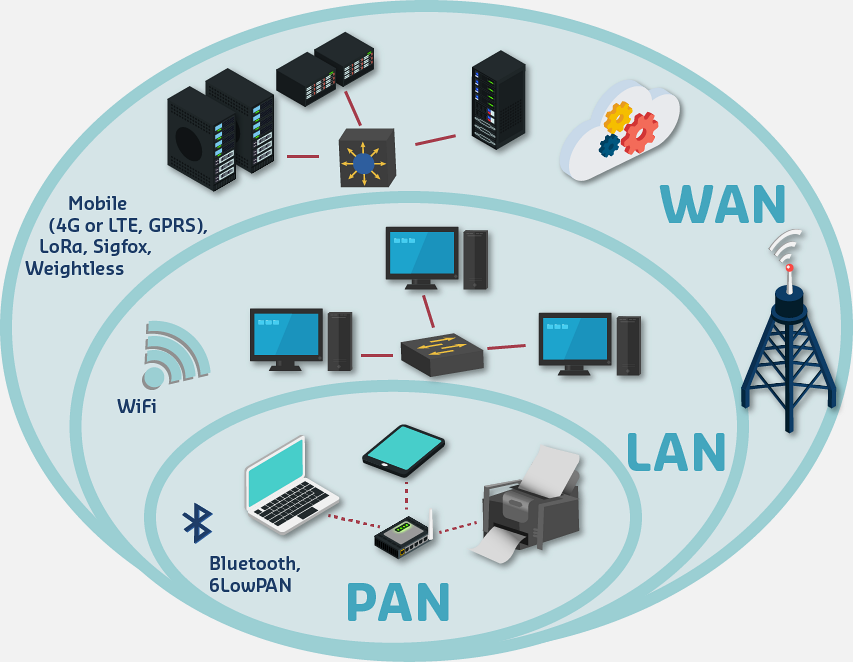
Networks are classified by how far they reach - like how we describe distances:
- Walking distance = PAN (Personal Area Network) - devices within arm’s reach (1-100 meters)
- Driving distance = LAN (Local Area Network) - devices in a building or campus (100m-1km)
- Flying distance = WAN (Wide Area Network) - devices across a city or country (1km to global)
| Network Type | Range | Example |
|---|---|---|
| PAN | 1-100m | Smartwatch connecting to phone |
| LAN | 100m-1km | Office Wi-Fi network |
| WAN | >1km | City-wide sensor network |
800.2 Bandwidth and Coverage Trade-offs
Today’s IoT networks are best explained by looking at the bandwidth and coverage of each network technology. Different protocols occupy different positions in the bandwidth-coverage space.
Quadrant 1 (High Bandwidth, High Coverage): Ideal but expensive - 5G Cellular: Ultimate performance, high cost - Use cases: Autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, video surveillance
Quadrant 2 (High Bandwidth, Low Coverage): Local high-speed - Wi-Fi: High data rates, limited range - Ethernet: Maximum bandwidth, wired - Use cases: Video streaming, building automation, industrial equipment
Quadrant 3 (Low Bandwidth, Low Coverage): Personal connectivity - Bluetooth/BLE: Short-range personal devices - Zigbee/Thread: Mesh networking for homes - Use cases: Wearables, home automation, medical devices
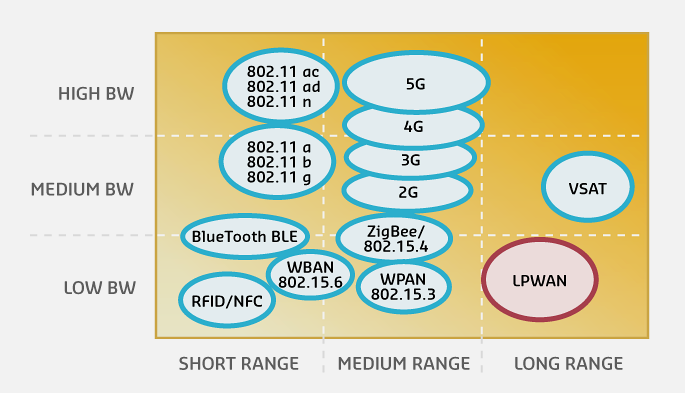
Quadrant 4 (Low Bandwidth, High Coverage): Wide-area sensing - LoRaWAN/Sigfox: Long range, low power, low cost - NB-IoT/LTE-M: Cellular-based LPWAN - Use cases: Agriculture, smart cities, asset tracking, utilities
800.3 Network Classification
Network technologies and protocols can be mapped to traditional network classifications as PAN (Personal Area Network), LAN (Local Area Network), and WAN (Wide Area Network).
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#E67E22', 'secondaryColor': '#16A085', 'tertiaryColor': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBkg': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBorder': '#16A085', 'fontSize': '13px'}}}%%
graph TB
subgraph WAN["WAN - Wide Area Network<br/>> 1 km range"]
WANTech["• LoRaWAN<br/>• Sigfox<br/>• NB-IoT<br/>• 5G"]
end
subgraph LAN["LAN - Local Area Network<br/>100m - 1km range"]
LANTech["• Wi-Fi<br/>• Ethernet<br/>• Wi-Fi HaLow"]
end
subgraph PAN["PAN - Personal Area Network<br/>1 - 100m range"]
PANTech["• Bluetooth LE<br/>• Zigbee<br/>• Thread<br/>• Z-Wave"]
end
style WAN fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style LAN fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style PAN fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
800.3.1 Personal Area Network (PAN)
PAN or Wireless PAN (WPAN) is a network with a small geographical area coverage, for devices such as sensors that require communication within a few meters.
Characteristics: - Range: 1-100 meters - Power: Low to very low (battery-powered) - Data rates: Low to medium (kbps to Mbps) - Topology: Star or mesh - Cost: Very low
Most Popular WPAN Technologies for IoT: - Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): Wearables, beacons, health devices - Zigbee: Home automation, lighting, security - Z-Wave: Home automation (competing with Zigbee) - Thread: IP-based mesh for smart homes - 6LoWPAN: IPv6 over low-power networks - NFC: Contactless payment, access control
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#E67E22', 'secondaryColor': '#16A085', 'tertiaryColor': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBkg': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBorder': '#16A085', 'fontSize': '13px'}}}%%
graph TB
Phone["Smartphone<br/>(Coordinator)"]
Watch["Smart Watch<br/>(BLE)"]
Headset["Headset<br/>(BLE)"]
Fitness["Fitness Tracker<br/>(BLE)"]
Beacon["BLE Beacon<br/>(Advertise only)"]
Phone --- Watch
Phone --- Headset
Phone --- Fitness
Phone -.->|Receives ads| Beacon
style Phone fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style Watch fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Headset fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Fitness fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Beacon fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
800.3.2 Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN provides connectivity within a building or campus, typically covering hundreds of meters to a few kilometers.
Characteristics: - Range: 100 meters - 1 km - Power: Mains powered (or PoE for Ethernet) - Data rates: Medium to very high (Mbps to Gbps) - Topology: Star (for Wi-Fi/Ethernet) - Cost: Low to medium
Most Popular LAN Technologies for IoT: - Wi-Fi (802.11 a/b/g/n/ac/ax): High bandwidth, building coverage - Ethernet (802.3): Wired connectivity, highest reliability - Wi-Fi HaLow (802.11ah): Extended range Wi-Fi for IoT
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#E67E22', 'secondaryColor': '#16A085', 'tertiaryColor': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBkg': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBorder': '#16A085', 'fontSize': '13px'}}}%%
graph TB
Router["Wi-Fi Router/AP"]
subgraph Wireless["Wi-Fi Devices"]
Cam["IP Camera"]
Thermo["Thermostat"]
Speaker["Smart Speaker"]
end
subgraph Wired["Ethernet Devices"]
NAS["NAS Storage"]
TV["Smart TV"]
Hub["IoT Hub"]
end
Router --- Cam
Router --- Thermo
Router --- Speaker
Router === NAS
Router === TV
Router === Hub
style Router fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style Cam fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Thermo fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Speaker fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style NAS fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style TV fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Hub fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
800.3.3 Wide Area Network (WAN)
WAN provides connectivity over large geographical areas, from city-wide to global coverage.
Characteristics: - Range: > 1 km to global - Power: Low (for LPWAN) to medium (for cellular) - Data rates: Very low to very high (bps to Gbps depending on technology) - Topology: Star (for LPWAN) or cellular - Cost: Low (for unlicensed LPWAN) to high (for cellular)
Most Popular WAN Technologies for IoT: - LoRaWAN: Unlicensed, long-range, low-power - Sigfox: Ultra-low bandwidth, very long range - NB-IoT: Cellular LPWAN, licensed spectrum - LTE-M: Cellular with higher bandwidth than NB-IoT - 5G: Next-generation cellular for massive IoT
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#E67E22', 'secondaryColor': '#16A085', 'tertiaryColor': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBkg': '#E8F6F3', 'clusterBorder': '#16A085', 'fontSize': '12px'}}}%%
graph TB
Cloud["Cloud Server<br/>(Internet)"]
subgraph City["Smart City WAN"]
GW1["LoRaWAN Gateway 1"]
GW2["LoRaWAN Gateway 2"]
S1["Parking Sensor"]
S2["Air Quality Monitor"]
S3["Water Meter"]
S4["Street Light"]
S5["Traffic Sensor"]
S6["Waste Bin Level"]
end
S1 -.->|"Long range<br/>2-15 km"| GW1
S2 -.-> GW1
S3 -.-> GW1
S4 -.-> GW2
S5 -.-> GW2
S6 -.-> GW2
GW1 -->|4G/Fiber| Cloud
GW2 -->|4G/Fiber| Cloud
style Cloud fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style GW1 fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style GW2 fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S1 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S2 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S3 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S4 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S5 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S6 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
800.4 Terminology Reference
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy | Low-power Bluetooth for IoT |
| LAN | Local Area Network | Building/campus network |
| NFC | Near Field Communication | Very short range (cm) |
| VSAT | Very Small Aperture Terminal | Satellite communication |
| BW | Bandwidth | Data carrying capacity |
| LoWPAN | Low-power Wireless PAN | IPv6 over low-power networks |
| PAN | Personal Area Network | Short-range network |
| WAN | Wide Area Network | Long-range network |
| ISM | Industrial, Scientific, Medical | Unlicensed radio bands |
| LPWAN | Low Power Wide Area Network | Long range, low power |
| RFID | Radio Frequency Identification | Tag-based identification |
| WPAN | Wireless Personal Area Network | Wireless PAN |
| MAC | Medium Access Control | Layer 2 addressing |
| PHY | Physical layer | Layer 1 signaling |
| CSMA/CA | Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance | Listen-before-talk |
| QoS | Quality of Service | Performance guarantees |
| PoE | Power over Ethernet | Power delivery via Ethernet |
800.5 Visual Reference Gallery
These AI-generated SVG figures provide alternative visual representations of network access and physical layer concepts. Each figure uses the IEEE color palette for consistency.
This visualization illustrates the fundamental trade-off in wireless IoT: higher bandwidth technologies like Wi-Fi offer shorter range, while LPWAN technologies sacrifice speed for kilometer-range coverage.
Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum helps explain why different IoT protocols use specific frequency bands and the propagation characteristics that result.
800.6 Summary
The IoT landscape uses multiple protocols simultaneously - often combining PAN (Zigbee sensors) to LAN (Wi-Fi gateway) to WAN (cellular/LPWAN) to Cloud. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each protocol enables optimal IoT system design.
Network Classifications: | Type | Range | Technologies | Use Cases | |——|——-|————–|———–| | PAN | 1-100m | BLE, Zigbee, Thread, Z-Wave | Wearables, smart home, sensors | | LAN | 100m-1km | Wi-Fi, Ethernet, HaLow | Building automation, cameras | | WAN | >1km | LoRaWAN, Cellular, Satellite | Smart cities, agriculture, utilities |
Bandwidth-Coverage Trade-off: - High bandwidth + High coverage = 5G (expensive) - High bandwidth + Low coverage = Wi-Fi, Ethernet - Low bandwidth + Low coverage = Bluetooth, Zigbee - Low bandwidth + High coverage = LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT
Protocol Selection Criteria: 1. No one-size-fits-all: Match protocol to application requirements 2. Future-proof: Consider technology lifecycle (avoid 2G/3G) 3. Total Cost of Ownership: Include subscription fees, not just hardware 4. Security: Encryption, authentication at physical layer where possible 5. Scalability: Can the network grow with your deployment? 6. Interoperability: Standard protocols vs proprietary solutions
Best Practices: - Combine multiple network types: PAN sensors -> LAN gateway -> WAN cloud - Design for growth - choose protocols that scale - Consider total cost including operations, not just hardware - Plan for technology evolution and migration paths
800.7 What’s Next?
Continue to Network Mechanisms to explore how networks handle addressing, routing, and data flow across these diverse physical and access layer technologies.


