%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': {'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'background': '#ffffff', 'mainBkg': '#2C3E50', 'secondBkg': '#16A085', 'tertiaryBkg': '#E67E22'}}}%%
flowchart TD
APL[Application Layer<br/>ZCL Clusters & Profiles] --> APS[APS Sublayer<br/>Endpoint Addressing]
APS --> ZDO[ZDO<br/>Device & Service Discovery]
ZDO --> NWK[Network Layer<br/>Mesh Routing + Security]
NWK --> MAC[MAC Layer<br/>802.15.4 CSMA/CA]
MAC --> PHY[Physical Layer<br/>2.4 GHz, 250 kbps]
SEC[Security] --> NWKSEC[Network Key<br/>AES-128]
SEC --> LINKSEC[Link Keys<br/>Per-Device]
style APL fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style NWK fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style MAC fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style PHY fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#333,color:#fff
style SEC fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
980 Zigbee Hands-On Labs
980.1 Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Implement Zigbee Security: Configure network keys, link keys, and Trust Center authentication
- Build Zigbee Networks: Set up coordinator, router, and end device configurations
- Develop Zigbee Applications: Use XBee modules, Zigbee2MQTT, and Python for prototyping
- Troubleshoot Zigbee Networks: Diagnose and resolve common deployment issues
- Deploy Real-World Applications: Apply Zigbee in smart lighting, security, and industrial IoT
What is this chapter? Hands-on exercises for building and deploying Zigbee networks with real hardware and software tools.
When to use: - When implementing Zigbee-based IoT projects - To learn practical Zigbee development workflows - For troubleshooting network deployment issues
Key Topics:
| Topic | Focus |
|---|---|
| XBee Modules | Arduino-based Zigbee prototyping |
| Zigbee2MQTT | Bridge Zigbee to MQTT ecosystems |
| Real-World Apps | Smart lighting, security, industrial |
| Troubleshooting | Common issues and solutions |
Prerequisites: - Zigbee Fundamentals - Basic understanding of mesh networking - Familiarity with IEEE 802.15.4
980.2 Prerequisites
Before diving into this chapter, you should be familiar with:
- Zigbee Fundamentals and Architecture: This chapter builds directly on Zigbee fundamentals, requiring understanding of device roles (Coordinator, Router, End Device), network formation, mesh routing with AODV, and the Zigbee protocol stack layers
- IEEE 802.15.4 Fundamentals: Hands-on Zigbee development requires knowledge of the underlying 802.15.4 PHY/MAC layer including channel selection, power modes, and frame structure for effective troubleshooting and optimization
- Network Topologies Fundamentals: Deploying and troubleshooting Zigbee networks requires understanding mesh topology behavior, self-healing mechanisms, and how to plan node placement for optimal coverage and reliability
980.3 Security Overview (Summary)
Security is mandatory in Zigbee and is provided at both the network and application layers.
980.3.1 Security Layers
- Network Layer: 128-bit AES network key encrypts all network-level traffic
- Application Layer: Link keys provide end-to-end encryption for sensitive data
980.3.2 Trust Center
The coordinator (Trust Center) distributes network keys, manages link keys, and authenticates devices during joining.
980.3.3 Security Features and Practices
- AES-128 encryption, sequence numbers (anti-replay), MIC integrity, device whitelisting, key refresh
- Use unique network keys, enable link keys for high-security devices, keep firmware updated, disable permit-join when not pairing, monitor for unknown devices
980.3.4 Zigbee Protocol Stack Architecture
980.4 Videos
980.4.1 Device Types
Zigbee networks consist of three device roles:
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': {'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'background': '#ffffff', 'mainBkg': '#2C3E50', 'secondBkg': '#16A085', 'tertiaryBkg': '#E67E22'}}}%%
flowchart TD
C[Coordinator 0x0000<br/>PAN ID: 0x1234<br/>Always On] --> R1[Router 0x0001<br/>Smart Light<br/>Mains Powered]
C --> R2[Router 0x0002<br/>Smart Plug<br/>Mains Powered]
C --> E1[End Device 0x0003<br/>Door Sensor<br/>Battery: 95%]
R1 --> R3[Router 0x0004<br/>Light Switch<br/>Mains Powered]
R1 --> E2[End Device 0x0005<br/>Temp Sensor<br/>Battery: 80%]
R2 --> E3[End Device 0x0006<br/>Motion Sensor<br/>Battery: 90%]
R3 --> E4[End Device 0x0007<br/>Window Sensor<br/>Battery: 85%]
R1 <--> R2
R2 <--> R3
style C fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style R1 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style R2 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style R3 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style E1 fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style E2 fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style E3 fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style E4 fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
980.4.1.1 Coordinator (ZC)
Role: Network formation, security key distribution, routing
Characteristics: - One per network (required) - Always mains-powered (never sleeps) - Initiates network, assigns addresses - Stores security keys - Example: Smart home hub, gateway
980.5 Hands-On: Building Zigbee Networks
This image from IIT Kharagpur’s NPTEL IoT course shows a Zigbee development board with labeled components for hands-on prototyping and wireless sensor network development.
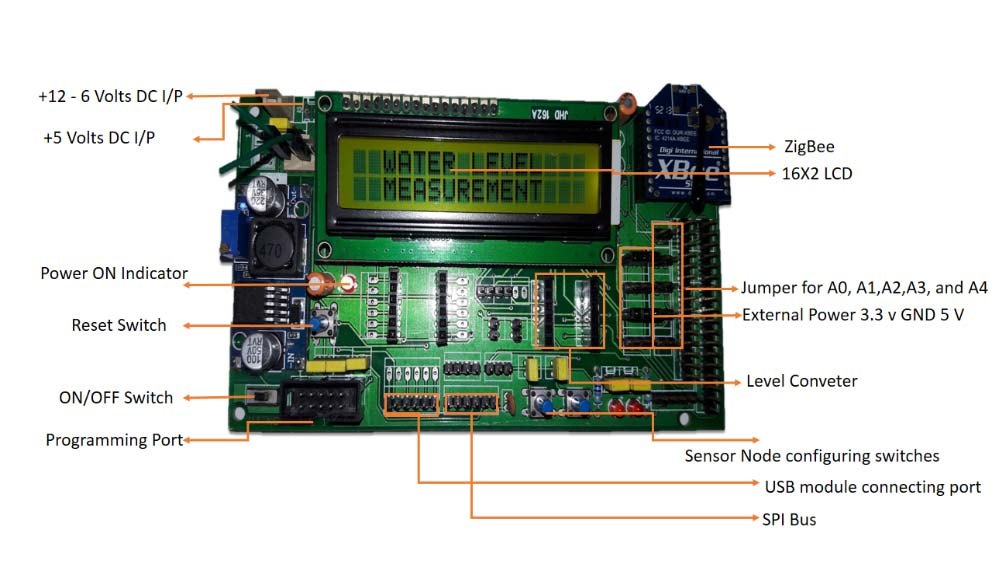
Source: NPTEL Internet of Things Course, IIT Kharagpur - Demonstrates typical Zigbee development board architecture for IoT prototyping
980.9 Visual Reference Gallery
These AI-generated figures provide alternative visual perspectives on Zigbee concepts.
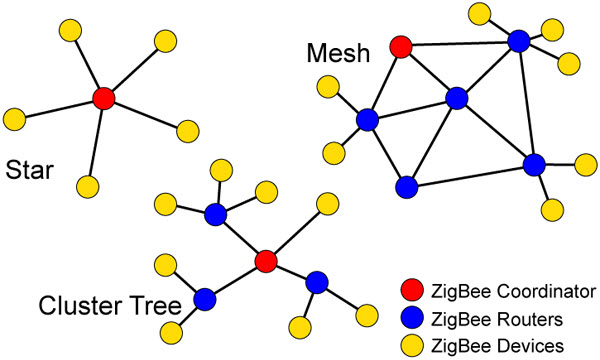
Zigbee Network Topology:
Zigbee Cluster Library:
Zigbee Protocol Stack:
Zigbee in IoT Landscape:
980.10 Summary
This chapter covered practical Zigbee implementation and future trends:
- Development Tools: Explored hardware platforms (XBee, Texas Instruments, Silicon Labs) and software frameworks (Z-Stack, EmberZNet, zigpy)
- Hands-On Labs: Built coordinator setup, sensor networks, custom clusters, OTA firmware updates, and network health monitoring systems
- Production Deployment: Analyzed real-world considerations including network planning, interference mitigation, and battery life optimization
- Home Automation Integration: Integrated Zigbee with Home Assistant, MQTT brokers, and cloud platforms for complete smart home solutions
- Matter and Zigbee Coexistence: Examined how Zigbee 3.0 devices can transition to Matter through firmware updates using dual-protocol chips
- Future Directions: Explored emerging trends including Green Power energy harvesting, improved commissioning, and multi-protocol ecosystems
- Troubleshooting Techniques: Applied diagnostic tools, channel analyzers, and network visualizations to identify and resolve mesh connectivity issues
980.11 What’s Next
The next chapter provides a Zigbee Comprehensive Review with interactive visualizations, deployment calculators, protocol comparison matrices, and knowledge check questions to reinforce your understanding of Zigbee concepts covered in previous chapters.







