%% fig-alt: "Cloud deployment models comparison showing characteristics of each type"
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'fontSize': '14px'}}}%%
graph LR
subgraph Public[Public Cloud]
Pub1[Shared Infrastructure]
Pub2[Low Cost]
Pub3[High Scalability]
end
subgraph Private[Private Cloud]
Priv1[Dedicated Infrastructure]
Priv2[High Security]
Priv3[Full Control]
end
subgraph Hybrid[Hybrid Cloud]
Hyb1[Best of Both]
Hyb2[Flexible Workloads]
Hyb3[Data Sovereignty]
end
subgraph Community[Community Cloud]
Comm1[Shared by Group]
Comm2[Common Requirements]
Comm3[Cost Sharing]
end
style Public fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Private fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style Hybrid fill:#E67E22,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style Community fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
272 Cloud Deployment Models for IoT
272.1 Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Compare Deployment Models: Evaluate public, private, hybrid, and community clouds for IoT workloads
- Design Hybrid Architectures: Architect solutions that balance cloud processing with edge and on-premises requirements
- Address Data Sovereignty: Apply deployment models to meet regulatory and compliance requirements
- Optimize Placement: Decide where to process data based on latency, cost, and security needs
272.2 Prerequisites
Before diving into this chapter, you should be familiar with:
- Cloud Computing Fundamentals: Understanding of NIST cloud model
- Cloud Service Models: Knowledge of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
272.3 Deployment Models Overview
272.4 Public Cloud
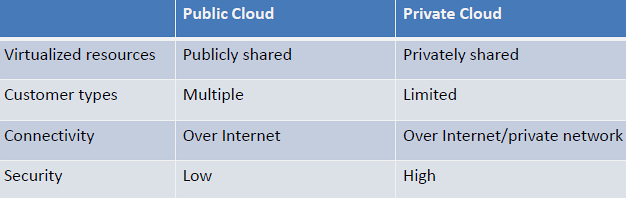
Owned and operated by third-party provider, shared among multiple customers.
Examples: AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud
IoT Use Cases:
- Rapid prototyping and development
- Startups with limited capital
- Variable workloads
- Global IoT deployments
Advantages:
- Zero upfront infrastructure cost
- Rapid scalability
- Global availability
- Managed services
Disadvantages:
- Less control over security
- Vendor lock-in concerns
- Compliance challenges for sensitive data
272.5 Private Cloud
Dedicated infrastructure for single organization, on-premises or hosted.
Examples: OpenStack, VMware vCloud, Microsoft Azure Stack
IoT Use Cases:
- Healthcare IoT (HIPAA compliance)
- Industrial IoT with proprietary processes
- Government/military applications
- High-security requirements
Advantages:
- Complete control over infrastructure and data
- Customization to specific requirements
- Enhanced security and privacy
- Regulatory compliance easier
Disadvantages:
- High capital expenditure
- Requires IT staff for management
- Limited scalability compared to public cloud
- Longer provisioning times
272.6 Public Cloud vs Private Cloud Trade-off
Option A: Public Cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP) - Multi-tenant shared infrastructure with pay-per-use pricing and unlimited scalability.
Option B: Private Cloud (On-premises, OpenStack) - Dedicated single-tenant infrastructure with full control and enhanced security.
Decision Factors:
Choose Public Cloud when: Rapid scaling is needed, capital budget is limited, workloads are variable, global distribution is required, or time-to-market is critical. Best for startups, prototypes, and non-sensitive IoT data.
Choose Private Cloud when: Regulatory compliance requires data residency (HIPAA, GDPR), intellectual property must stay on-premises, latency requirements demand local processing, or predictable high-volume workloads make owned infrastructure cheaper over 3+ years.
Consider Hybrid when: Sensitive data (PHI, trade secrets) needs private storage while analytics and ML benefit from public cloud scalability. The orchestration complexity adds 20-30% operational overhead but provides best-of-both-worlds flexibility.
272.7 Hybrid Cloud
Combination of public and private clouds with orchestration between them.
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'fontSize': '14px'}}}%%
graph TB
subgraph IoT_Edge["IoT Edge Devices"]
D1[Medical Device<br/>PHI Data]
D2[Industrial Sensor<br/>Proprietary]
D3[Public Sensors<br/>Weather]
end
subgraph Private["Private Cloud (On-Premises)"]
PDB[(Sensitive Data<br/>PHI, Trade Secrets)]
PApp[Compliance Apps<br/>HIPAA, ISO]
PAuth[Identity &<br/>Access Control]
end
subgraph Public["Public Cloud (AWS/Azure)"]
PubML[ML Training<br/>Anonymized Data]
PubScale[Auto-Scaling<br/>Compute]
PubStorage[Archive Storage<br/>S3 Glacier]
end
subgraph Hybrid_Orchestration["Hybrid Orchestration Layer"]
DataGov[Data Governance<br/>Classification]
Sync[Sync Engine<br/>VPN/Direct Connect]
Workload[Workload<br/>Placement]
end
D1 -->|Encrypted| Private
D2 -->|Encrypted| Private
D3 -->|Public Data| Public
Private <-->|VPN Tunnel| Hybrid_Orchestration
Public <-->|API Gateway| Hybrid_Orchestration
Hybrid_Orchestration -->|Anonymized<br/>Only| PubML
Hybrid_Orchestration -->|Burst Traffic| PubScale
style Private fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff,stroke-width:3px
style Public fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff,stroke-width:3px
style Hybrid_Orchestration fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff,stroke-width:3px
272.7.1 Real-World Hybrid IoT Example: Hospital Patient Monitoring
Scenario: 500-bed hospital with 2,000 patient monitoring devices.
Data Classification:
| Data Type | Volume | Latency Req | Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time vitals (PHI) | 2K devices x 1 msg/sec | <1 sec | Private Cloud (HIPAA) |
| Historical trends (anonymized) | 100 GB/day | Minutes OK | Public Cloud (cheap storage) |
| ML training data (de-identified) | 10 TB dataset | Hours OK | Public Cloud (GPU clusters) |
| Alerts & alarms (critical) | 50 events/day | <500 ms | Private Cloud (reliability) |
Hybrid Architecture Decision:
Private Cloud (On-Premises): - What: Dell VxRail hyper-converged infrastructure (200 TB, 50 VMs) - Why: HIPAA requires PHI under direct control, low latency for critical alarms - Cost: $250K CAPEX + $30K/year maintenance - Pros: Full control, <1ms latency, meets compliance
Public Cloud (AWS): - What: S3 Glacier (archives), SageMaker (ML training), Lambda (batch processing) - Why: Elastic capacity for ML training, 90% cheaper storage for 7-year retention - Cost: $5K/month ($60K/year OPEX) - Pros: Infinite scalability, pay-per-use, access to advanced ML tools
Cost Comparison (5-year TCO):
| Approach | 5-Year Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud Only | $900K | Compliance audit costs +$50K/year |
| Private Cloud Only | $610K | Cannot scale for ML training |
| Hybrid (Recommended) | $910K | Best balance: compliance + scalability |
Trade-off Analysis: Hybrid costs $10K more over 5 years but provides ML innovation, 10x scalability for pandemic response, and disaster recovery.
272.8 Edge Processing vs Cloud Processing
Option A: Edge Processing - Run analytics on gateways near IoT devices. Sub-100ms latency, operates during network outages, reduces bandwidth costs.
Option B: Cloud Processing - Send all data to cloud for centralized analytics. Unlimited compute for ML/AI, unified dashboards, simpler device firmware.
Decision Factors:
Choose Edge when: Latency requirements are under 100ms (industrial control), bandwidth costs are significant (cellular IoT at $0.50-2.00/MB), network connectivity is unreliable, or data privacy requires local processing.
Choose Cloud when: Advanced ML models require GPU clusters unavailable at edge, cross-device analytics need centralized data, historical analysis spans months/years, or edge hardware constraints limit processing capability.
Bandwidth savings calculation: 1000 sensors at 1 reading/second = 86.4M readings/day. Raw to cloud: 8.64 GB/day. Edge aggregation (5-minute averages): 28.8 MB/day. Annual savings: $1,500-6,300 per 1000 sensors on cellular.
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'fontSize': '12px'}}}%%
sequenceDiagram
participant S as Sensor
participant E as Edge/Gateway
participant I as Internet
participant C as Cloud Platform
participant A as Analytics
participant R as Response
Note over S,R: Complete Cloud IoT Data Journey
S->>E: 0-10ms: Sensor reading
Note over E: Edge processing:<br/>Filter, aggregate,<br/>local threshold check
E->>I: 10-50ms: MQTT publish
Note over I: Network latency varies:<br/>Wi-Fi: 10-50ms<br/>Cellular: 50-200ms
I->>C: 50-200ms: Cloud ingestion
Note over C: IoT Hub receives,<br/>validates, routes
C->>A: 200-500ms: Stream processing
Note over A: Real-time analytics,<br/>ML inference
A->>R: 500-1000ms: Action triggered
Note over R: Alert sent,<br/>actuator command
R-->>S: 1000-2000ms: Feedback loop
Note over S,R: Total round-trip: 1-2 seconds<br/>(too slow for real-time control)
272.9 IoT Scale Cost Comparison
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'fontSize': '12px'}}}%%
flowchart TB
subgraph Scale1["100 Devices (Prototype)"]
S1_Best["Best: SaaS<br/>ThingSpeak Free Tier<br/>$0-30/month"]
S1_Alt["Alt: PaaS<br/>AWS IoT Core<br/>$50/month"]
end
subgraph Scale2["10,000 Devices (Production)"]
S2_Best["Best: PaaS<br/>AWS IoT Core + Lambda<br/>$200-500/month"]
S2_Alt["Alt: IaaS<br/>Self-managed MQTT<br/>$300-600/month"]
end
subgraph Scale3["1M Devices (Enterprise)"]
S3_Best["Best: IaaS or Hybrid<br/>On-prem + Cloud burst<br/>$5K-20K/month"]
S3_Alt["Consider: Dedicated<br/>Private cloud + edge<br/>$10K-50K/month"]
end
Scale1 --> Scale2
Scale2 --> Scale3
style S1_Best fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S2_Best fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style S3_Best fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
272.10 Hospital Deployment Knowledge Check
272.11 Summary
This chapter covered cloud deployment models for IoT:
- Public Cloud: Best for startups, variable workloads, rapid prototyping
- Private Cloud: Best for compliance, security-sensitive applications
- Hybrid Cloud: Best balance of compliance and scalability - recommended for most enterprise IoT
- Edge-Cloud Integration: Use edge for real-time (<100ms), cloud for analytics and storage
- Scale Considerations: Optimal deployment model changes with device count
272.12 What’s Next?
Now that you understand deployment models, continue with:
- Cloud Security for IoT - Learn about IAM, encryption, and security best practices
- Cloud Platforms and Message Queues - Compare AWS, Azure, and messaging technologies
