%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'fontSize': '14px'}}}%%
graph TB
ROOT["Weightless LPWAN<br/>(Open Standard)"]
ROOT --> W1["Weightless-W<br/>(TV White Space)"]
ROOT --> W2["Weightless-N<br/>(ISM Band, Ultra-Narrow)"]
ROOT --> W3["Weightless-P<br/>(ISM Band, Bi-directional)"]
W1 --> F1["Spectrum: TV bands<br/>Range: 5 km<br/>Data: High<br/>Power: Medium"]
W2 --> F2["Spectrum: Sub-GHz ISM<br/>Range: 3 km<br/>Data: Low (uplink only)<br/>Power: Ultra-low"]
W3 --> F3["Spectrum: Sub-GHz ISM<br/>Range: 2 km<br/>Data: Medium<br/>Power: Low (bi-dir)"]
NOTE["Key Advantages:<br/>✓ No vendor lock-in<br/>✓ Spectrum flexibility<br/>✓ Multiple variants for different needs<br/>✓ Open standard (anyone can implement)"]
ROOT -.-> NOTE
style ROOT fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,stroke-width:3px,color:#fff
style W1 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style W2 fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style W3 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,stroke-width:2px,color:#fff
style F1 fill:#d4edda,stroke:#16A085,stroke-width:1px,color:#000
style F2 fill:#fff3cd,stroke:#E67E22,stroke-width:1px,color:#000
style F3 fill:#e2e3e5,stroke:#7F8C8D,stroke-width:1px,color:#000
style NOTE fill:#e2e3e5,stroke:#16A085,stroke-width:1px,color:#000
1145 Weightless LPWAN Overview
1145.1 Introduction
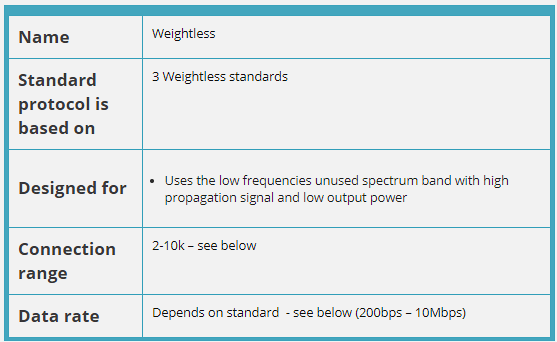
Weightless is an open-standard LPWAN technology developed by the Weightless Special Interest Group (Weightless SIG), a non-profit standards organization. Unlike Sigfox (proprietary, single operator) or NB-IoT (cellular-licensed), Weightless offers an open standard that any vendor can implement. The technology comes in three variants—Weightless-W, Weightless-N, and Weightless-P—each optimized for different use cases and spectrum allocations.
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Understand the three Weightless variants (W, N, P) and their differences
- Explain the Weightless SIG’s open-standard philosophy
- Identify appropriate use cases for Weightless technologies
- Understand TV White Space spectrum utilization
1145.2 Prerequisites
Before diving into this chapter, you should be familiar with:
- LPWAN Fundamentals: Understanding core LPWAN concepts including long-range communication, ultra-low power operation, and trade-offs between range, data rate, and battery life provides essential context for Weightless technologies
- Networking Basics: Knowledge of wireless communication fundamentals, frequency bands, modulation schemes, and network topologies helps understand Weightless variants’ technical differences
- LoRaWAN: Familiarity with LoRaWAN architecture and capabilities provides a comparison baseline for evaluating Weightless’s market positioning and technical approach
Imagine you’re shopping for a car, and the dealer says “We have three models: the Economy for city driving, the Truck for hauling cargo, and the Luxury for long highway trips.” Each vehicle is optimized for different needs. Weightless is similar—it’s not one technology but three different versions (Weightless-W, Weightless-N, and Weightless-P), each designed for different IoT use cases.
Why three versions? Because there’s no “one size fits all” in IoT. Some applications need to send data both ways (sensors receiving commands), some only need to send (simple tracking), some need TV white space spectrum, and some need bidirectional communication with good battery life. Rather than forcing everyone to use one design, Weightless offers options.
The key innovation of Weightless-W is using TV white spaces—unused TV broadcast frequencies that became available when TV went digital. Imagine empty radio channels that no one is using—Weightless-W borrows these for long-range IoT communication. This gives excellent range and penetration through buildings.
Weightless-N is the simplest variant—one-way communication only (device to base station), ultra-low power, perfect for “report sensor reading every hour” applications. Weightless-P adds two-way communication, making it suitable for devices that need to receive commands or confirmations.
| Term | Simple Explanation |
|---|---|
| Weightless-W | Original variant using TV white space spectrum (bidirectional) |
| Weightless-N | Narrow-band variant—one-way communication only (ultra low power) |
| Weightless-P | Two-way communication variant—best balance of features |
| TV White Space | Unused TV broadcast frequencies available for unlicensed use |
| Open Standard | Anyone can implement—no single company controls it |
| ISM Band | Industrial, Scientific, Medical—unlicensed radio frequencies |
| Bidirectional | Two-way communication (device can send and receive) |
| Unidirectional | One-way only (device only sends, doesn’t receive) |
1145.3 The Weightless SIG
The Weightless Special Interest Group was founded in 2012 to develop open standards for LPWAN communications. The organization includes members from across the IoT ecosystem: chipset manufacturers, network operators, system integrators, and end users.
Philosophy:
Weightless networks follow a star topology similar to LoRaWAN and Sigfox. End devices communicate directly with base stations (not through mesh routing), which reduces complexity and power consumption. The core network handles authentication, data routing, and application server integration.
Weightless-W’s use of TV white space spectrum provides excellent range and building penetration due to lower frequencies (470-790 MHz). However, TV white space availability varies by region and requires database coordination to avoid interfering with TV broadcasts.
- Open standard: Anyone can implement (unlike Sigfox)
- Multiple variants: Different solutions for different needs
- Spectrum flexibility: TV White Space and ISM bands
- Vendor choice: No single vendor lock-in
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': {'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#E67E22', 'secondaryColor': '#16A085', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D'}}}%%
flowchart TD
START(["Select Weightless Variant"]) --> Q1{"Need high<br/>data throughput?"}
Q1 -->|Yes| Q2{"TV White Space<br/>available?"}
Q1 -->|No| Q3{"Need downlink<br/>commands?"}
Q2 -->|Yes| WW["Weightless-W<br/>TV White Space<br/>High throughput<br/>5 km range"]
Q2 -->|No| WP2["Consider<br/>Weightless-P"]
Q3 -->|Yes| WP["Weightless-P<br/>ISM band<br/>Bi-directional<br/>Medium power"]
Q3 -->|No| WN["Weightless-N<br/>ISM band<br/>Uplink only<br/>Ultra-low power"]
style WW fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style WN fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style WP fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
This decision tree helps select the appropriate Weightless variant based on application requirements: throughput needs, spectrum availability, and bidirectional communication.
1145.4 Videos
1145.5 Use Cases
Weightless is designed for applications requiring: - Wide area coverage (urban and rural) - Low power consumption (multi-year battery life) - Low data rate communications - Cost-effective connectivity - Open standards (no vendor lock-in)
Example applications: - Traffic sensors (original motivating application) - Environmental monitoring - Smart agriculture - Asset tracking - Smart metering - Industrial sensing
1145.6 Weightless Variants Comparison
| Feature | Weightless-W | Weightless-N | Weightless-P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrum | TV White Space (470-790 MHz) | Sub-GHz ISM | Sub-GHz ISM (868/915 MHz) |
| Data Rate | 1 kbps - 10 Mbps | 100 bps | 200 bps - 100 kbps |
| Range | 5+ km | 3 km | 2-5 km |
| Direction | Bidirectional | Uplink only | Bidirectional |
| Power | Medium | Ultra-low | Low |
| Status | Limited adoption | Discontinued | Active |
| Best For | High bandwidth, rural | Simple sensors | Most IoT applications |
Key Insight: Weightless-P has emerged as the primary variant due to its balance of features and simpler deployment (no TV White Space database required).
1145.7 Summary
This chapter introduced the Weightless LPWAN family and its three variants:
- Weightless is an open-standard LPWAN technology developed by the Weightless SIG
- Three variants address different use cases: W (TV White Space), N (ultra-simple uplink), P (balanced bidirectional)
- Open standard philosophy enables multiple vendors and avoids lock-in
- Weightless-P is the most actively developed variant, operating in ISM bands with adaptive data rates
1145.8 What’s Next
Continue learning about Weightless with these related chapters:
- Next: Weightless Technical Details - Python implementations, adaptive data rate, and power calculations
- Then: Weightless Market Comparison - Ecosystem analysis, market positioning, and decision frameworks
- Related: LPWAN Comparison - Side-by-side analysis of all LPWAN technologies


