%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': {'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D', 'background': '#ffffff', 'mainBkg': '#2C3E50', 'secondBkg': '#16A085', 'tertiaryBkg': '#E67E22'}}}%%
graph TD
START{Need LPWAN<br/>Connectivity?}
START -->|Yes| Q1{Need global<br/>roaming?}
START -->|No| OTHER[Use Wi-Fi/BLE/<br/>Cellular]
Q1 -->|Yes| CELL[NB-IoT/LTE-M<br/>Cellular LPWAN]
Q1 -->|No| Q2{Cellular coverage<br/>exists?}
Q2 -->|No| Q3{Can deploy<br/>gateways?}
Q2 -->|Yes| Q4{Need 99.9%<br/>reliability?}
Q3 -->|Yes| LORA_PRIV[LoRaWAN<br/>Private Network]
Q3 -->|No| NOMATCH[No suitable<br/>LPWAN option]
Q4 -->|Yes| CELL2[NB-IoT/LTE-M<br/>Carrier SLA]
Q4 -->|No| Q5{Messages > 140/day<br/>or payload > 12 bytes?}
Q5 -->|Yes| Q6{Want network<br/>control?}
Q5 -->|No| Q7{Sigfox coverage<br/>available?}
Q6 -->|Yes| LORA_PUB[LoRaWAN<br/>Public/Private]
Q6 -->|No| CELL3[NB-IoT/LTE-M<br/>Managed service]
Q7 -->|Yes| SIGFOX[Sigfox<br/>Subscription]
Q7 -->|No| LORA_FALLBACK[LoRaWAN<br/>or cellular]
style START fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style Q1 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Q2 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Q3 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Q4 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Q5 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Q6 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Q7 fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style CELL fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style CELL2 fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style CELL3 fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style LORA_PRIV fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style LORA_PUB fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style LORA_FALLBACK fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style SIGFOX fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style OTHER fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style NOMATCH fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
1051 LPWAN Technology Selection
1051.1 LPWAN Technology Selection Decision Tree
Choosing the right LPWAN technology depends on your deployment model, coverage needs, and application requirements. Use this decision tree to guide your selection:
{fig-alt=“LPWAN technology selection decision tree guiding users through key questions: global roaming needs, cellular coverage availability, gateway deployment capability, reliability requirements, message frequency, and network control preferences. Leads to recommendations for NB-IoT/LTE-M (cellular), LoRaWAN (private/public), or Sigfox based on requirements.”}
1051.2 LPWAN Technology Comparison Matrix
Use this comprehensive comparison to evaluate LPWAN options for your use case:
| Factor | LoRaWAN | Sigfox | NB-IoT | LTE-M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (Urban) | 2-5 km | 3-10 km | 1-10 km | 1-10 km |
| Range (Rural) | 15 km | 30-50 km | 10-15 km | 10-15 km |
| Data Rate | 0.3-50 kbps | 100 bps (UL) 600 bps (DL) |
Up to 250 kbps | Up to 1 Mbps |
| Bandwidth | 125-500 kHz | 100 Hz (UNB) | 180 kHz | 1.4 MHz |
| Messages/Day | Unlimited | 140 UL / 4 DL | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Payload Size | 243 bytes max | 12 bytes (UL) 8 bytes (DL) |
1600 bytes | 1600 bytes |
| Latency | 1-5 seconds | 2-6 seconds | 1-10 seconds | 10-15 ms |
| Battery Life | 5-15 years | 10-20 years | 5-10 years | 5-10 years |
| Spectrum | Unlicensed ISM (868/915 MHz) |
Unlicensed ISM (868/902 MHz) |
Licensed LTE (800-2600 MHz) |
Licensed LTE (700-2600 MHz) |
| Deployment | Private or public | Public operator | Carrier network | Carrier network |
| Coverage | DIY or operator | Limited (70 countries) | Global (100+ countries) | Global (100+ countries) |
| Device Cost | $3-10 | $2-5 | $10-30 | $15-40 |
| Gateway Cost | $200-1500 (buy once) | N/A (operator) | N/A (carrier) | N/A (carrier) |
| Subscription | $0-1/device/year (private = $0) |
$1-2/device/year | $1-5/device/month | $2-10/device/month |
| 10-Year Cost (1000 devices) |
$15K (private) $25K (public) |
$25K | $300K | $500K |
| Mobility | Poor (stationary) | Poor (stationary) | Good (limited handoff) | Excellent (full handoff) |
| Downlink | Yes (Class A/B/C) | Yes (4 msgs/day) | Yes (unlimited) | Yes (unlimited) |
| Reliability | 85-95% (Class A) 97-99% (confirmed) |
95-98% (3x repeat) | 99.9% (TCP-like) | 99.9% (TCP-like) |
| QoS | No | No | Yes (3GPP) | Yes (3GPP) |
| Security | AES-128 | AES-128 | LTE security | LTE security |
| Standardization | LoRa Alliance | Sigfox (proprietary) | 3GPP standard | 3GPP standard |
| Firmware Updates | Yes (FUOTA) | No (too limited) | Yes (TCP/UDP) | Yes (TCP/UDP) |
| Best For | Private networks Agriculture Smart buildings Fixed sensors |
Ultra-low cost Infrequent updates Simple sensors Low volume |
Mission-critical Smart cities Utilities Reliable delivery |
Asset tracking Fleet management Mobile devices Voice support |
Option A (LoRaWAN Private): Zero recurring connectivity cost, full data sovereignty, 2-15 km range per gateway. Upfront: 5 gateways x $500 = $2,500 + $15,000 sensors. 10-year TCO for 1,000 devices: ~$17,500 ($1.75/device/year). Requires gateway deployment and backhaul.
Option B (Cellular LPWAN): No infrastructure deployment, global roaming, 99.9% carrier SLA reliability. 10-year TCO for 1,000 devices: $20,000 hardware + $300,000 subscriptions = $320,000 ($32/device/year). Licensed spectrum eliminates interference.
Decision Factors: Choose LoRaWAN Private for fixed-location deployments (agriculture, utilities, smart buildings) where you control the premises and want minimal recurring costs. Choose Cellular LPWAN for mobile assets (fleet tracking, logistics), mission-critical reliability requirements, or deployments spanning multiple countries/regions where gateway deployment is impractical.
Option A (SF7): Data rate 5.5 kbps, airtime 36 ms for 12-byte payload, range 2-3 km urban, battery: 500,000+ messages on 2xAA cells. Link budget: +137 dB. Best throughput.
Option B (SF12): Data rate 0.25 kbps, airtime 1,810 ms for 12-byte payload (50x longer), range 8-15 km, battery: 10,000 messages on same cells. Link budget: +157 dB (+20 dB gain). Maximum range.
Decision Factors: Choose SF7-SF9 for urban deployments with good gateway density, high-frequency reporting (>10 messages/hour), or when battery life is critical. Choose SF10-SF12 for rural deployments, deep indoor penetration, or when gateway infrastructure is sparse. Use ADR (Adaptive Data Rate) to automatically optimize: devices start at SF12 for reliability, network server adjusts downward as link quality permits.
1051.3 Interactive Tool: LPWAN Technology Selector
Use this interactive tool to determine the best LPWAN technology for your IoT deployment. Answer the questions below based on your requirements, and the tool will recommend LoRaWAN, Sigfox, or NB-IoT/LTE-M.
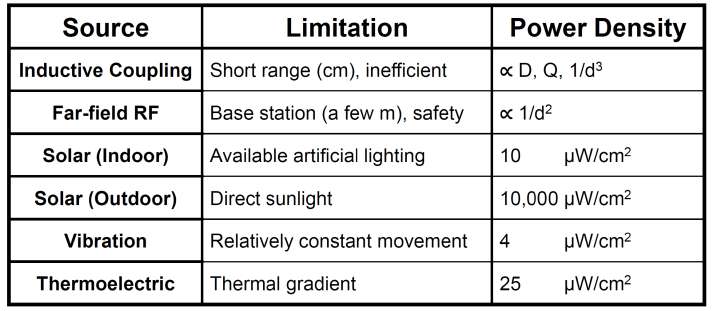
Source: Stanford University IoT Course - Energy harvesting enables battery-free LPWAN sensors. Note the 1000x difference between indoor (10 uW/cm2) and outdoor solar (10,000 uW/cm2), explaining why most solar-powered IoT is outdoor.
Understanding energy efficiency is critical for battery-powered IoT deployments. Energy per bit varies dramatically across wireless protocols, creating a 100x difference between the most and least efficient options:
| Protocol | Energy (nJ/bit) | Range | Data Rate | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | 50-100 | ~100m | 54+ Mbps | High bandwidth, power available |
| BLE | 15-30 | ~10m | 1-2 Mbps | Short range, frequent small packets |
| Zigbee | 40-60 | ~100m | 250 kbps | Mesh networks, moderate data |
| LoRa | 1000-5000 | 10+ km | 0.3-50 kbps | Long range, infrequent data |
| NB-IoT | 500-1000 | Cellular | 250 kbps | Licensed spectrum, reliability |
| Sigfox | 500-2000 | 10+ km | 100 bps | Ultra-low data, long range |
Key insights: 1. Long range costs more per bit - LoRa uses 50-100x more energy per bit than BLE 2. Total energy matters - Sending 1KB via LoRa may still be efficient if it avoids gateway infrastructure 3. Protocol overhead varies - Consider header sizes for small payloads 4. Sleep current dominates - A device sleeping 99% of the time may use more energy sleeping than transmitting!
Key Insight: Energy per bit is NOT the whole story. Total energy consumption depends on your data volume and range requirements.
Example Scenarios:
Scenario 1: Smart Water Meter (1 reading/day, 12 bytes)
Wi-Fi: 12 bytes x 8 bits x 75 nJ/bit = 7,200 nJ/msg -> Battery life: 1-2 years
LoRa SF12: 12 bytes x 8 bits x 1200 nJ/bit = 115,200 nJ/msg -> Battery life: 10+ years
Why LoRa wins: Despite 16x worse energy/bit, LoRa's longer range means no Wi-Fi routers neededScenario 2: Fitness Tracker (continuous data, 1 KB/hour)
BLE: 1000 bytes x 8 bits x 25 nJ/bit = 200,000 nJ/msg -> Battery life: days (rechargeable OK)
LoRa SF7: 1000 bytes x 8 bits x 1000 nJ/bit = 8,000,000 nJ/msg -> Battery life: weeks (not months!)
Why BLE wins: For continuous data, BLE's 40x better energy/bit matters more than LoRa's rangeDecision Framework:
- Low data volume (< 1 KB/day) + Long range needed -> Choose LoRa/NB-IoT
- Total energy dominated by fixed overhead (radio warmup, sync)
- Higher energy/bit acceptable for infrequent transmissions
- Example: Soil moisture sensor sending 20 bytes/hour across 5 km farm
- High data volume (> 1 MB/day) + Short range acceptable -> Choose Wi-Fi/BLE
- Total energy dominated by data transmission
- Lower energy/bit becomes critical
- Example: Smartwatch syncing health data to phone every 5 minutes
- Medium data (1-100 KB/day) + Medium range -> Choose Zigbee/NB-IoT
- Balance between energy/bit and range
- Example: Smart thermostat updating temperature every 15 minutes
Rule of Thumb: Choose based on total energy for your data volume and range, not just energy/bit. A 100x worse energy/bit protocol can still have 10x better battery life if you only send 1/1000th the data.
The Mistake: Believing that using LoRa or any LPWAN technology automatically guarantees multi-year battery life, then being surprised when batteries drain in weeks.
Why It Happens: LPWAN marketing emphasizes “10+ year battery life” without clarifying that this assumes proper power management: aggressive sleep modes, infrequent transmissions (1-4 per hour), and avoiding continuous sensing. Developers who poll sensors frequently or use Class C mode negate all power benefits.
The Fix: Calculate your actual power budget before deployment. A LoRa radio transmitting at SF12 consumes 120mA for 1.3 seconds per message. At 1 message per hour with proper sleep (1uA), you get 10 years. At 1 message per minute, you get 6 months. At continuous Class C listening (15mA), you get 2 weeks on 2xAA batteries.
The Mistake: Selecting LPWAN technology based solely on range claims, then discovering fundamental protocol mismatches with application requirements (e.g., Sigfox’s 140 messages/day limit for a parking sensor that changes state 50 times daily).
Why It Happens: LPWAN technologies appear similar at a high level (long range, low power) but have vastly different design centers: LoRaWAN for flexibility and private networks, Sigfox for ultra-simple sensors with infrequent updates, NB-IoT for carrier-grade reliability and mobility.
The Fix: Match technology to your specific requirements: (1) Message frequency: Sigfox limits 140/day, LoRaWAN limited by duty cycle (~500-2000/day at SF10), NB-IoT unlimited. (2) Bidirectional needs: Sigfox allows only 4 downlinks/day, LoRaWAN and NB-IoT are symmetric. (3) Mobility: Only LTE-M and NB-IoT support handoff. (4) Coverage: NB-IoT requires carrier infrastructure, LoRaWAN can be self-deployed.
1051.4 Cost Analysis Examples
Understanding total cost of ownership is critical for LPWAN selection:
Scenario 1: Smart Agriculture - 1,000 Soil Sensors (10 years)
| Option | Hardware | Infrastructure | Subscription (10yr) | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoRaWAN (Private) | $10K | $7.5K (5 gateways) | $0 | $17.5K |
| LoRaWAN (Public) | $10K | $0 | $15K ($1.50/yr/device) | $25K |
| Sigfox | $5K | $0 | $20K ($2/yr/device) | $25K |
| NB-IoT | $25K | $0 | $300K ($30/yr/device) | $325K |
Winner: LoRaWAN private (lowest cost for stationary, rural deployment)
Scenario 2: Fleet Tracking - 500 Trucks (5 years, global)
| Option | Hardware | Infrastructure | Subscription (5yr) | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoRaWAN | $5K | $0 | $0 | $5K + No global coverage |
| Sigfox | $2.5K | $0 | $5K | $7.5K + Limited coverage |
| NB-IoT | $15K | $0 | $150K | $165K Best option |
| LTE-M | $20K | $0 | $250K | $270K Fallback option |
Winner: NB-IoT (only option with global mobility and reliable coverage)
Scenario 3: Smart City Parking - 10,000 Sensors (10 years)
| Option | Hardware | Infrastructure | Subscription (10yr) | Total Cost | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoRaWAN | $50K | $30K (20 gateways) | $0 | $80K | 85-95% |
| Sigfox | $30K | $0 | $200K | $230K | 95-98% |
| NB-IoT | $250K | $0 | $3M | $3.25M | 99.9% |
Winner: Depends on reliability requirement - Best cost: LoRaWAN ($80K but 85-95% reliability) - Best reliability: NB-IoT ($3.25M but 99.9% reliability) - Compromise: Sigfox ($230K with 95-98% reliability)
1051.5 Selection Checklist
Use this checklist to narrow down your LPWAN choice:
1. Coverage Requirements - [ ] Do you have good cellular (4G/5G) coverage? Consider NB-IoT/LTE-M - [ ] Is deployment in rural/remote areas? Consider LoRaWAN - [ ] Need global roaming? NB-IoT/LTE-M only option
2. Deployment Model - [ ] Can you deploy/maintain gateways? LoRaWAN feasible - [ ] Want zero infrastructure management? NB-IoT/LTE-M or Sigfox - [ ] Need full network control/privacy? LoRaWAN private
3. Application Requirements - [ ] Messages > 140/day? NB-IoT/LTE-M or LoRaWAN - [ ] Payload > 12 bytes? Not Sigfox - [ ] Reliability must be 99%+? NB-IoT/LTE-M - [ ] Downlink commands required? Not Sigfox (4/day limit)
4. Device Characteristics - [ ] Devices are mobile? LTE-M or NB-IoT - [ ] Devices are stationary? Any LPWAN works - [ ] Need firmware updates OTA? LoRaWAN or NB-IoT/LTE-M
5. Cost Constraints - [ ] Minimize upfront cost? Sigfox (lowest device cost) - [ ] Minimize operational cost? LoRaWAN private (no subscription) - [ ] Budget allows $2-5/device/month? NB-IoT/LTE-M acceptable
6. Scale and Timeline - [ ] < 100 devices? Any option (small scale) - [ ] 100-10,000 devices? Consider private LoRaWAN ROI - [ ] > 10,000 devices? Private LoRaWAN or negotiate carrier bulk pricing
7. Future-Proofing - [ ] Need 5G migration path? NB-IoT/LTE-M (3GPP standards) - [ ] Concerned about operator bankruptcy? LoRaWAN (own infrastructure) - [ ] Want open standards? LoRaWAN (LoRa Alliance) or NB-IoT (3GPP)
1051.6 Real-World Deployment Examples
LoRaWAN Success Stories: - Agriculture: 100,000+ acre farm with 5,000 soil sensors, 20 gateways, $0 ongoing cost - Smart Building: 500-sensor private network, complete data privacy, gateway on-premise - Campus Tracking: University asset tracking with full network control
Sigfox Success Stories: - Utility Meters: Water/gas meters with 1 reading/day, $1/year/meter - Simple Sensors: Temperature/humidity monitoring, minimal data, ultra-low cost - Geolocation: GPS tracking with Sigfox Atlas (< 140 msgs/day)
NB-IoT Success Stories: - Smart Cities: Barcelona parking sensors, 99.9% reliability for payment systems - Utilities: Smart meters with carrier SLA, regulatory compliance - Industrial: Factory monitoring requiring guaranteed message delivery
LTE-M Success Stories: - Fleet Management: Global shipping container tracking with roaming - Medical Devices: Wearable monitors with voice fallback capability - Asset Tracking: High-value equipment requiring real-time location
1051.7 Summary
This chapter covered LPWAN technology selection:
- Decision tree: Navigate from requirements to recommended technology
- Comparison matrix: Detailed specifications for LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT, LTE-M
- Interactive selector: Tool to evaluate your specific use case
- Cost analysis: TCO examples for different deployment scenarios
- Selection checklist: Questions to narrow down your choice
1051.8 What’s Next
Continue to LPWAN Link Budget for range calculation tools and link budget analysis, or explore LPWAN Pitfalls for common mistakes to avoid.
LPWAN Fundamentals Series: - LPWAN Overview - Introduction and basics - LPWAN Knowledge Checks - Test your understanding - LPWAN Link Budget - Range calculations - LPWAN Pitfalls - Common mistakes to avoid
