647 Layered Network Models
647.1 Overview
Layered network models are the foundation of all network communication, dividing complex networking tasks into manageable, independent layers. This section covers the theoretical OSI model, the practical TCP/IP model, addressing schemes, and hands-on implementation.
647.2 Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Understand Network Standards: Explain why standards and protocols enable global connectivity
- Compare OSI and TCP/IP Models: Differentiate between the seven-layer OSI and four-layer TCP/IP models
- Explain Encapsulation: Describe how data moves through protocol layers
- Apply IoT Reference Models: Understand IoT-specific architectural frameworks
- Configure MAC and IP Addressing: Work with hardware and network layer addresses
- Implement IPv4/IPv6: Configure and troubleshoot both IP versions
- Resolve Addresses: Understand ARP and how MAC/IP mapping works
647.3 Chapter Contents
This topic is covered in three focused chapters:
647.3.1 1. Layered Models Fundamentals
Core concepts of layered networking - Why standards matter, OSI 7-layer model, TCP/IP 4-layer model, protocol data units (PDUs), encapsulation/decapsulation processes, and IoT reference models.
Topics covered:
- Networking standards and interoperability
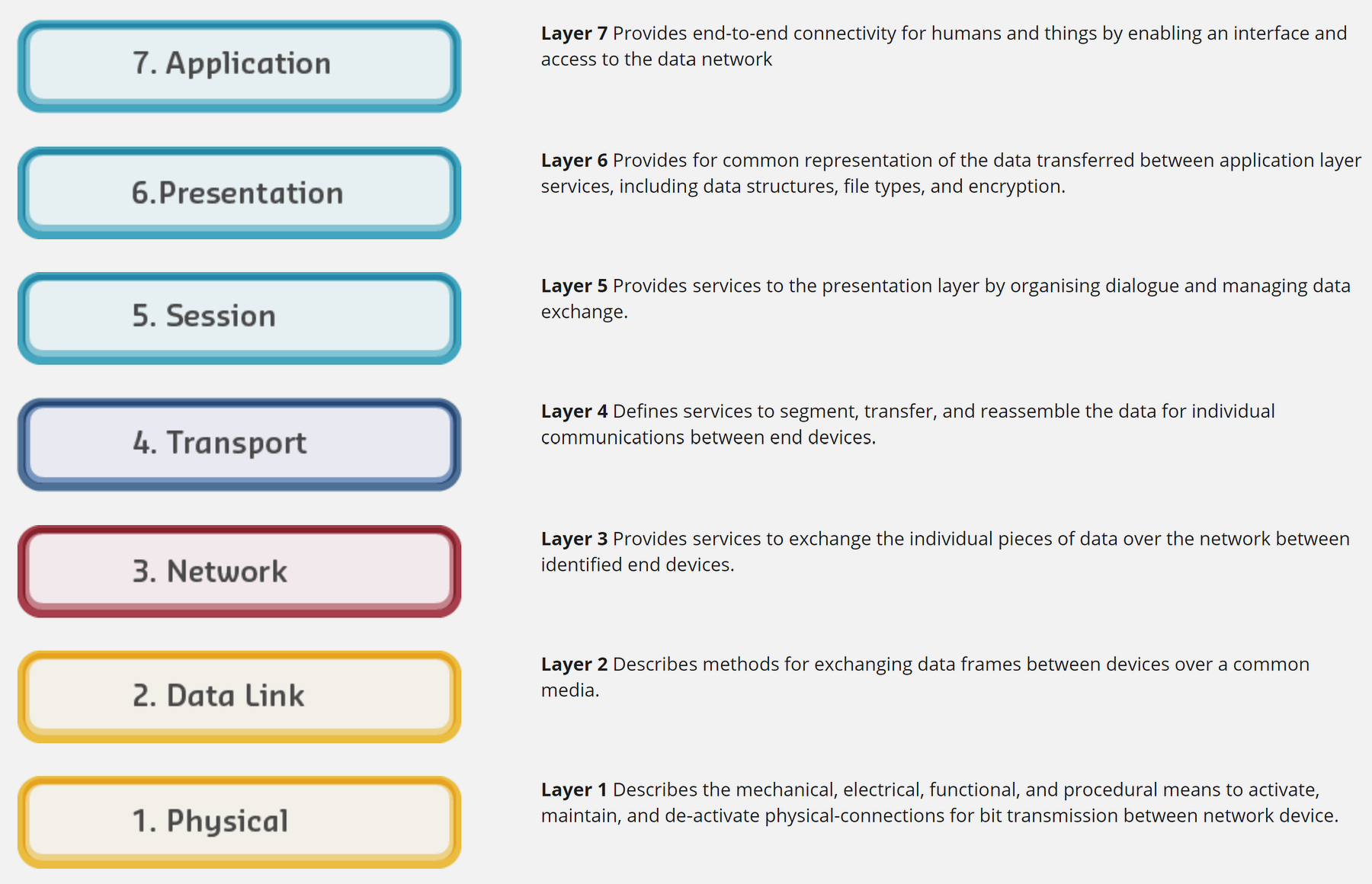
- OSI 7-layer model (theoretical framework)
- TCP/IP 4-layer model (practical implementation)
- Protocol data units at each layer
- Encapsulation and decapsulation
- IoT reference models (Cisco 7-Level, ITU)
- Layer-by-layer troubleshooting
647.3.2 2. Addressing and Implementation
Hands-on addressing and configuration - MAC addressing, IPv4/IPv6 addressing, subnet masks, ARP protocol, and practical labs for configuring network addresses.
Topics covered:
- MAC address structure and types
- IPv4 addressing and subnet masks
- IPv6 addressing and benefits for IoT
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Hands-on configuration labs
- Python implementation examples
647.3.3 3. Review and Knowledge Checks
Comprehensive review and assessment - Knowledge checks, quiz questions, worked examples, and visual reference galleries to reinforce understanding.
Topics covered:
- Key concepts summary
- Scenario-based knowledge checks
- Protocol stack selection worked example
- Visual reference gallery
- Further learning resources
647.4 Quick Reference
The OSI model (7 layers) is a theoretical framework used for teaching and troubleshooting. The TCP/IP model (4 layers) is the practical implementation that powers the internet. Both use encapsulation - wrapping data in headers as it moves down the stack, and decapsulation - unwrapping headers as it moves up.
Key mapping: TCP/IP Application = OSI Layers 5-7, TCP/IP Transport = OSI Layer 4, TCP/IP Internet = OSI Layer 3, TCP/IP Network Access = OSI Layers 1-2.
| Layer Type | Addressing | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Data Link (L2) | MAC addresses (48-bit) | Local network segment |
| Network (L3) | IP addresses (IPv4: 32-bit, IPv6: 128-bit) | End-to-end routing |
647.5 Prerequisites
Before diving into this section, you should be familiar with:
- Networking Basics: Understanding fundamental networking concepts, topologies, and protocols
- IoT Protocols Fundamentals: Basic knowledge of IoT communication protocols
647.6 What’s Next
After completing these chapters, continue with:
- Routing Fundamentals: How packets find their way across networks
- Transport Protocols: TCP vs UDP characteristics
- Network Mechanisms: Packet switching and datagrams

