%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': {'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#7F8C8D'}}}%%
flowchart TD
Start(["Application Domain?"]) --> Domain{"Environment?"}
Domain -->|"Factory/Industrial"| IND["Industrial Kit"]
Domain -->|"Body-worn"| WEAR["Wearable Kit"]
IND --> Scale{"Scale/Budget?"}
Scale -->|"Enterprise ($400+)"| SIEM["Siemens IOT2050<br/>Full industrial stack"]
Scale -->|"Small-scale (~$100)"| OPTA["Arduino Opta<br/>Micro-PLC"]
WEAR --> App{"Application?"}
App -->|"Fashion/Art"| LILY["LilyPad Arduino<br/>Sew-able"]
App -->|"Health/Medical"| MAX["Maxim Health<br/>Medical-grade"]
style Start fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style SIEM fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style OPTA fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style LILY fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style MAX fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
1591 Prototyping Kits: Industrial and Wearable
1591.1 Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Evaluate Industrial IoT Platforms: Compare Siemens IOT2050 and Arduino Opta for factory automation and industrial control
- Select Wearable Development Kits: Choose between LilyPad Arduino and Maxim Health platforms based on application requirements
- Understand Industrial Requirements: Assess temperature range, voltage levels, certifications, and protocol support for industrial deployments
- Plan Health Monitoring Prototypes: Leverage medical-grade sensors and validated algorithms for wearable health devices
- Navigate Regulatory Considerations: Understand certification paths for industrial and medical device prototypes
1591.2 Prerequisites
Before diving into this chapter, you should be familiar with:
- Specialized Prototyping Kits Overview: Understanding the kit ecosystem architecture helps you evaluate industrial and wearable kit capabilities
- Prototyping Hardware: Knowledge of microcontrollers and sensors enables you to assess industrial-grade component requirements
- Sensor Fundamentals: Understanding sensor types helps evaluate health monitoring sensor integration
1591.3 Introduction
Industrial IoT and wearable health monitoring represent specialized domains with stringent requirements. Industrial kits must handle harsh environments, industrial protocols, and safety certifications. Wearable health kits require medical-grade sensors, validated algorithms, and consideration of regulatory pathways. This chapter explores leading platforms in both domains.
Industrial IoT Kits work in factories and harsh environments. They typically include: - Wide temperature range (-20°C to +60°C) - Industrial voltages (24V inputs) - Protocol support (Modbus, BACnet, OPC UA) - DIN rail mounting for industrial enclosures
Wearable Health Kits monitor body signals. They typically include: - Medical-grade sensors (heart rate, SpO2) - Small form factor for body-worn use - Low power for all-day battery life - Validated algorithms for accuracy
Example: Arduino Opta controls factory relays using Modbus. Maxim Health Platform measures heart rate with FDA-quality sensors.
1591.4 Industrial IoT Kits
1591.4.1 Siemens IOT2050
Description: Industrial-grade edge computing platform for IIoT applications.
Components: - ARM Cortex-A53/A72 processor - Industrial I/O modules - Industrial Ethernet - Real-time capable - Wide voltage input
Development: - Industrial Linux - Node-RED - Docker containers - CODESYS PLC runtime
Use Cases: - Factory automation - Predictive maintenance - Industrial edge computing - Protocol gateways
Strengths: - Industrial-grade reliability - Professional software stack - Real-time capability - Wide temperature range
Limitations: - Expensive ($400+) - Complex for beginners - Overkill for simple projects
1591.4.2 Arduino Opta
Description: Industrial micro PLC with IoT connectivity.
Components: - STM32H7 microcontroller - 8 digital inputs - 4 relay outputs - Ethernet and Wi-Fi - RS-485 interface - DIN rail mounting
Development: - Arduino IDE - PLC programming (61131-3) - Industrial protocols (Modbus, OPC UA) - Cloud integration
Use Cases: - Small-scale automation - Building management - Industrial control - Process monitoring
Strengths: - Arduino ecosystem - Industrial form factor - Multiple programming options - Competitive pricing ($100)
Limitations: - Limited I/O - New product (limited community)
1591.4.3 Industrial Kit Comparison
| Feature | Siemens IOT2050 | Arduino Opta |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | ARM Cortex-A53/A72 | STM32H7 |
| Price | $400+ | ~$100 |
| OS | Industrial Linux | Bare metal/Arduino |
| Protocols | Full industrial stack | Modbus, OPC UA |
| I/O | Expansion modules | 8 DI, 4 relay |
| Target | Enterprise IIoT | Small-scale automation |
| Learning Curve | High | Medium |
1591.5 Knowledge Check
1591.6 Wearable and Health Monitoring Kits
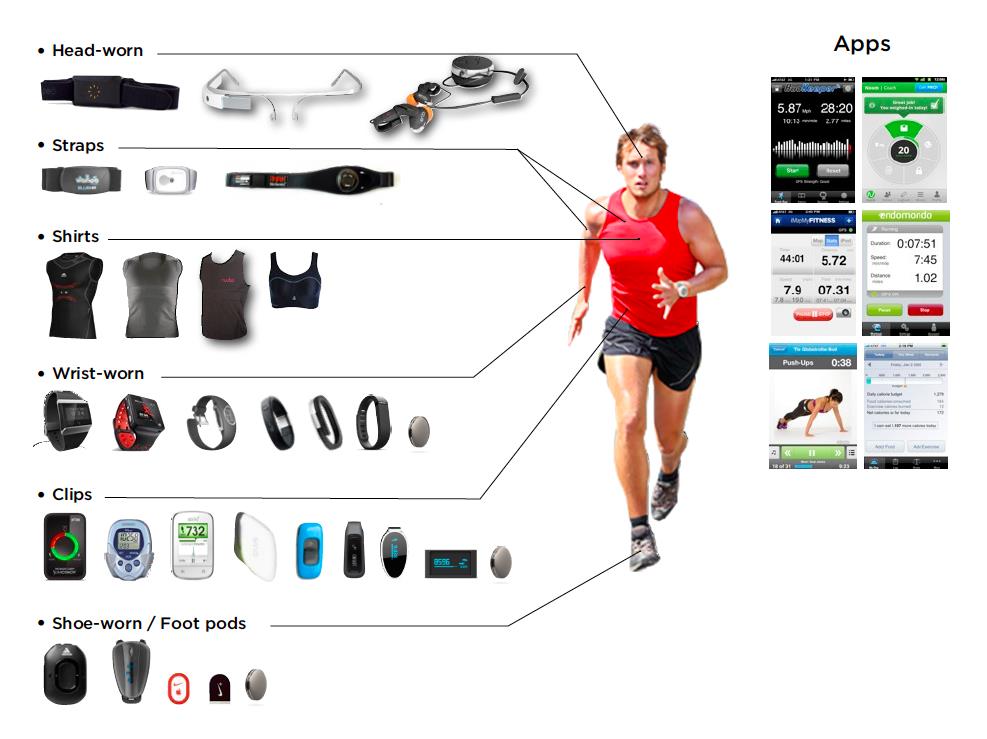
Source: University of Edinburgh - Principles and Design of IoT Systems. This taxonomy helps prototypers understand the full landscape of wearable form factors when designing new wearable IoT products.
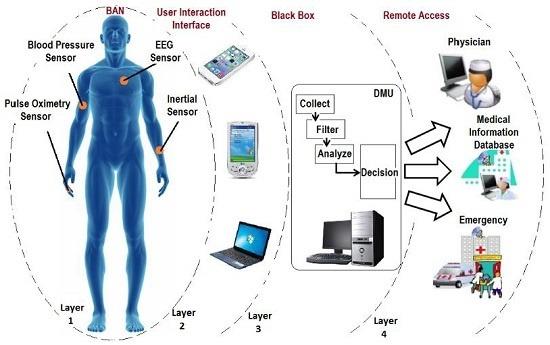
Source: University of Edinburgh - Principles and Design of IoT Systems. This BAN architecture illustrates the complete system design needed for health monitoring wearables - from body sensors through local processing to cloud connectivity.
1591.6.1 LilyPad Arduino Wearable Kit
Description: Sew-able electronics platform for wearable projects.
Components: - LilyPad Arduino main board - LED modules - Accelerometer - Light sensor - Conductive thread - Battery holder
Development: - Arduino IDE - Specialized wearable libraries - Low-power modes
Use Cases: - E-textiles - Wearable art - Fashion tech - Educational wearables
Strengths: - Sew-able design - Washable components - Creative applications - Beginner-friendly
Limitations: - Limited processing power - Basic sensors - Durability concerns
1591.6.2 Maxim Integrated Health Sensor Platform
Description: Medical-grade health monitoring development kit.
Components: - MAX32664 biometric hub - MAX30101 heart rate/SpO2 sensor - MAX30205 temperature sensor - MAX32630 microcontroller - Accelerometer - Bluetooth
Development: - mbed OS - Algorithm library - Mobile app SDKs
Use Cases: - Health wearables - Fitness trackers - Medical device prototypes - Clinical research
Strengths: - Medical-grade sensors - Validated algorithms - Low power - FDA-quality components
Limitations: - Expensive - Complex integration - Regulatory considerations
1591.6.3 Wearable Kit Comparison
| Feature | LilyPad Arduino | Maxim Health Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Target | E-textiles, fashion | Medical/fitness |
| Sensors | Basic (light, motion) | Medical-grade (HR, SpO2) |
| Price | $50-100 | $200-400 |
| Form Factor | Sew-able | Module-based |
| Algorithms | DIY | Validated |
| Regulatory | Consumer | FDA-pathway |
1591.7 Industrial vs Wearable Considerations
1591.7.1 Key Differences
| Aspect | Industrial Kits | Wearable Kits |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Factory, harsh | Body-worn, personal |
| Temperature | -20°C to +60°C | Ambient (body temp) |
| Power | Mains/industrial | Battery (small) |
| Size | DIN rail modules | Miniaturized |
| Protocols | Modbus, OPC UA | BLE, proprietary |
| Certification | Industrial (CE, UL) | Medical (FDA, CE) |
| Durability | Vibration, EMI | Water, sweat |
1591.8 Regulatory Considerations
1591.8.1 Industrial Certifications
Industrial IoT kits targeting production must address:
- CE Marking (Europe): Electromagnetic compatibility, safety
- UL Listing (North America): Safety certification
- IEC 61131 compliance for PLC programming
- ATEX/IECEx for hazardous environments
Kit Advantage: Pre-certified kits (Arduino Opta, Siemens IOT2050) include certifications, saving months of testing.
1591.8.2 Medical Device Regulations
Health monitoring wearables face additional requirements:
- FDA 510(k) (US): Medical device clearance
- CE Medical (Europe): Medical device directive
- Clinical validation: Algorithm accuracy studies
- Data privacy: HIPAA, GDPR compliance
Kit Advantage: Maxim Health Platform uses FDA-quality sensors and validated algorithms, providing a foundation for regulatory submissions.
Prototyping kits are for development and research. Production medical devices require formal regulatory submissions, clinical validation, and quality management systems. Consult regulatory experts before commercializing health monitoring products.
1591.9 Summary
- Siemens IOT2050 provides enterprise-grade industrial edge computing with Linux, Docker, real-time capability, and comprehensive industrial protocol support for factory automation and predictive maintenance
- Arduino Opta offers accessible industrial automation with Arduino ecosystem familiarity, RS-485/Modbus support, relay outputs, and DIN rail mounting at a competitive price point
- LilyPad Arduino enables creative wearable projects with sew-able, washable components for e-textiles, fashion tech, and educational applications
- Maxim Integrated Health Sensor Platform provides medical-grade sensors (heart rate, SpO2, temperature) with validated algorithms for health monitoring prototypes targeting FDA-quality accuracy
- Industrial kits emphasize harsh environment operation, industrial protocols, and safety certifications, while wearable kits emphasize miniaturization, low power, and body-worn comfort
- Regulatory considerations differ significantly: industrial kits focus on CE/UL safety certifications, while medical wearables require FDA/CE medical device pathways
1591.10 What’s Next
The next chapter covers AI, Wireless, and Energy Harvesting Kits, exploring computer vision platforms, wireless communication kits, and energy harvesting solutions for battery-free IoT deployments.
Kit Overview: - Specialized Prototyping Kits Overview - Complete kit ecosystem - Kit Selection and Best Practices - Selection criteria
Industrial: - Industrial Protocols - Modbus, OPC UA - Edge Computing - Industrial edge
Wearable: - Sensor Fundamentals - Health sensors - BLE Fundamentals - Wearable connectivity
