%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#fff'}}}%%
graph TB
subgraph MCU["Microcontroller (MCU)"]
MCU_CPU[CPU Core<br/>16-240 MHz]
MCU_RAM[RAM<br/>2KB-512KB]
MCU_Flash[Flash<br/>32KB-2MB]
MCU_GPIO[GPIO/ADC/Timers]
MCU_COMM[UART/I2C/SPI]
end
subgraph MPU["Microprocessor (MPU)"]
MPU_CPU[CPU Core<br/>1-2 GHz Multi-core]
MPU_EXT[External Components]
MPU_RAM_EXT[RAM<br/>1-8 GB]
MPU_STORAGE[Storage<br/>16-64 GB]
MPU_OS[Full OS<br/>Linux/Android]
end
MCU_CPU --- MCU_RAM
MCU_CPU --- MCU_Flash
MCU_CPU --- MCU_GPIO
MCU_CPU --- MCU_COMM
MPU_CPU --- MPU_EXT
MPU_EXT --- MPU_RAM_EXT
MPU_EXT --- MPU_STORAGE
MPU_CPU --- MPU_OS
style MCU fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style MPU fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style MCU_CPU fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style MPU_CPU fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
1531 Microcontrollers vs Microprocessors
1531.1 Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Distinguish between microcontrollers (MCUs) and microprocessors (MPUs)
- Select the appropriate platform based on project requirements
- Understand hybrid approaches and System-on-Chip designs
- Apply selection criteria for power, performance, and cost trade-offs
1531.2 Understanding the Difference
Understanding the distinction between microcontrollers and microprocessors is fundamental to selecting appropriate hardware platforms for IoT prototyping.
1531.3 Microcontrollers (MCUs)
Definition: Integrated circuits containing processor core, memory (RAM and Flash), and peripherals (GPIO, ADC, timers, communication interfaces) in a single chip.
1531.3.1 Characteristics
- All-in-one: Complete computer on a chip
- Low power: Designed for embedded, battery-operated applications
- Real-time: Deterministic timing, no operating system overhead (or RTOS)
- Low cost: Typically $1-$20 per unit
- Limited resources: KB-MB of RAM, MHz clock speeds
- Bare-metal or RTOS: Often programmed directly or with real-time OS
1531.3.2 Popular MCU Families
- ARM Cortex-M: STM32, Nordic nRF52, NXP Kinetis
- AVR: Arduino Uno/Mega (ATmega328P, ATmega2560)
- ESP32/ESP8266: Wi-Fi-enabled MCUs
- PIC: Microchip PIC microcontrollers
- MSP430: Texas Instruments ultra-low-power MCUs
1531.3.3 Ideal For
- Battery-powered devices
- Real-time control applications
- Simple sensing and actuation
- Cost-sensitive products
- Space-constrained designs
1531.3.4 Examples
- Wearable fitness tracker
- Smart thermostat
- Wireless sensor node
- Home automation switch
1531.4 Microprocessors (MPUs)
Definition: Processor cores requiring external components (RAM, storage, power management) to function, typically running full operating systems.
1531.4.1 Characteristics
- High performance: GHz clock speeds, multi-core
- Rich OS: Linux, Windows IoT, Android
- Abundant resources: GB RAM, GB storage
- Peripheral interfaces: USB, HDMI, Ethernet, etc.
- Higher power: Watts vs milliwatts for MCUs
- Complex software stack: Full OS, drivers, middleware
1531.4.2 Popular MPU Platforms
- ARM Cortex-A: Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone
- x86/x64: Intel Edison, UP Board
- Application Processors: Qualcomm, MediaTek (smartphones/tablets)
1531.4.3 Ideal For
- Edge computing and AI/ML inference
- Rich user interfaces (displays, touchscreens)
- Complex data processing
- Internet connectivity and web services
- Video/audio processing
- Gateway and hub applications
1531.4.4 Examples
- Smart home hub
- Video surveillance system
- Industrial gateway
- Autonomous robot
1531.5 Hybrid Approaches
1531.5.1 MPU + MCU
Combining microprocessor for high-level processing with microcontroller for real-time control.
Example: Raspberry Pi (MPU) running Linux for web interface and cloud connectivity, Arduino (MCU) handling motor control with precise timing.
1531.5.2 System-on-Chip (SoC)
Integrated circuits combining application processor cores with MCU cores and peripherals.
Examples: - ESP32: Dual-core processor with Wi-Fi/Bluetooth - STM32MP1: Cortex-A7 + Cortex-M4 in single chip - i.MX RT: Cortex-M7 at 600 MHz with rich peripherals
1531.6 Selection Criteria
%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#fff'}}}%%
flowchart TD
Start[Start Platform Selection] --> Q1{Need Wi-Fi/BLE?}
Q1 -->|Yes| Q2{Need Full Linux OS?}
Q1 -->|No| Q3{Battery Powered?}
Q2 -->|Yes| RPi[Raspberry Pi<br/>MPU + Rich OS]
Q2 -->|No| ESP32[ESP32<br/>MCU + Wi-Fi/BLE]
Q3 -->|Yes| Q4{Real-time Critical?}
Q3 -->|No| Q5{Many GPIO Needed?}
Q4 -->|Yes| STM32[STM32 Low-Power<br/>MCU + Ultra-low Sleep]
Q4 -->|No| ESP32_Battery[ESP32 Deep Sleep<br/>MCU + Wi-Fi]
Q5 -->|Yes| Mega[Arduino Mega<br/>54 Digital + 16 Analog]
Q5 -->|No| Uno[Arduino Uno<br/>Beginner Friendly]
style Start fill:#7F8C8D,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style RPi fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style ESP32 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style STM32 fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style Mega fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
style Uno fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
1531.6.1 Decision Factors
| Requirement | Choose MCU | Choose MPU |
|---|---|---|
| Computational | Simple sensing/actuation | Complex analytics, ML |
| Power | Battery-powered, years of life | Mains-powered |
| Real-Time | Hard real-time (motor control) | Soft real-time (UI) |
| Connectivity | UART, SPI, I2C | Ethernet, USB host, video |
| Software | Bare-metal or RTOS | Full OS with apps |
| Cost | Price-sensitive, high volume | Feature-rich, lower volume |
1531.7 Knowledge Check
1531.8 Reference Diagrams
The following diagrams provide additional context for understanding hardware platform architectures.
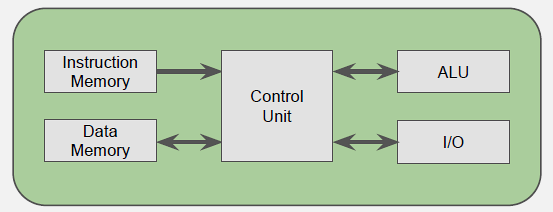
Block diagram showing how all components are integrated on a single MCU chip.
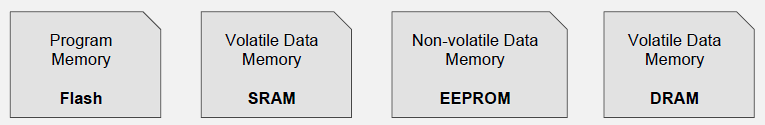
Comparison of memory types used in embedded systems.
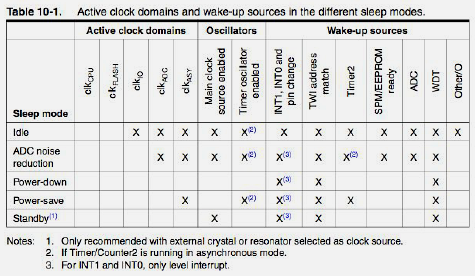
Power management through various sleep modes is critical for battery-powered IoT devices.
1531.9 What’s Next
Continue to Common Hardware Platforms for a deep dive into Arduino, ESP32, and Raspberry Pi platforms with hands-on simulators.
