%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#fff'}}}%%
flowchart TD
Dev[Developer] --> IDE[IDE/Editor]
IDE --> IDE1[Arduino IDE:<br/>Beginner-friendly]
IDE --> IDE2[VS Code + PlatformIO:<br/>Professional]
IDE --> IDE3[CLion:<br/>Advanced C++]
IDE1 --> Compiler[Compiler/Toolchain]
IDE2 --> Compiler
IDE3 --> Compiler
Compiler --> Flash[Flash/Program<br/>Device]
Flash --> Debug[Debugging Tools]
Debug --> D1[Serial Monitor:<br/>Print statements]
Debug --> D2[JTAG Debugger:<br/>Breakpoints, step]
Debug --> D3[Logic Analyzer:<br/>Signal inspection]
Debug --> Version[Version Control]
Version --> Git[Git + GitHub]
style IDE2 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style D2 fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style Git fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
1550 IoT Development Tools and Environments
1550.1 Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Use Development Environments: Configure and utilize IDEs, compilers, and build systems for embedded development
- Apply Debugging Techniques: Use JTAG debuggers, serial monitors, and logic analyzers to diagnose firmware issues
- Implement Version Control: Apply Git workflows appropriate for embedded software and hardware co-development
- Understand Toolchain Architecture: Explain the role of compilers, linkers, and programmers in embedded development
- Select Testing Frameworks: Choose appropriate testing tools for embedded and IoT applications
1550.2 Prerequisites
Before diving into this chapter, you should be familiar with:
- Programming Paradigms: Understanding different programming approaches helps contextualize tool selection
- Electronics Basics: Hardware knowledge is essential for debugging and hardware-software integration
1550.3 Introduction
Modern development tools have dramatically increased IoT developer productivity. From powerful IDEs with intelligent code completion to sophisticated debugging tools and automated testing frameworks, the ecosystem supports rapid iteration from prototype to production.
1550.3.1 Essential IoT Programming Tools
1550.4 Code Editors and IDEs
1550.4.1 Visual Studio Code
Universal code editor with extensive IoT support through extensions.
Key Extensions: - PlatformIO IDE - Arduino - C/C++ IntelliSense - Python - GitLens
Features: - IntelliSense autocomplete - Integrated terminal - Git integration - Debugging support - Remote development (SSH to Raspberry Pi)
Strengths: - Lightweight yet powerful - Highly customizable - Large extension ecosystem - Free and open-source
1550.4.2 Arduino IDE 2.0
Modernized Arduino development environment.
Improvements over 1.x: - Code autocomplete - Debugger integration - Library dependency management - Dark mode - Multiple file tabs
1550.4.3 CLion
Professional C/C++ IDE by JetBrains.
Features: - Advanced code analysis - Refactoring tools - Embedded debugger support - CMake integration - Unit testing integration
Best For: Professional embedded development, complex C++ projects.
1550.4.4 Alternative Editors
Atom, Sublime Text: Alternative lightweight editors with IoT plugin ecosystems.
1550.5 Build Systems
1550.5.1 Make
Traditional Unix build automation tool.
Makefile Example:
CC = avr-gcc
CFLAGS = -Os -DF_CPU=16000000UL -mmcu=atmega328p
TARGET = firmware
all: $(TARGET).hex
$(TARGET).hex: $(TARGET).elf
avr-objcopy -O ihex -R .eeprom $< $@
$(TARGET).elf: main.o sensor.o
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $^
%.o: %.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c $<
upload: $(TARGET).hex
avrdude -p atmega328p -c arduino -P /dev/ttyUSB0 -b 115200 -U flash:w:$<
clean:
rm -f *.o *.elf *.hex1550.5.2 CMake
Cross-platform build system generator.
CMakeLists.txt Example:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(IoTProject)
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
add_executable(firmware
src/main.cpp
src/sensor.cpp
src/communication.cpp
)
target_include_directories(firmware PRIVATE include)
target_link_libraries(firmware wiringPi pthread)1550.5.3 PlatformIO Build System
Unified build system for embedded platforms.
platformio.ini:
[env:esp32]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32dev
framework = arduino
build_flags =
-D DEBUG=1
-D SENSOR_PIN=4
lib_deps =
adafruit/Adafruit BME280 Library
knolleary/PubSubClient1550.6 Version Control Systems
1550.6.1 Git
Distributed version control system, industry standard.
Essential Commands:
# Initialize repository
git init
# Clone existing repository
git clone https://github.com/user/iot-project.git
# Check status
git status
# Stage changes
git add src/sensor.cpp
# Commit
git commit -m "Add temperature sensor support"
# Push to remote
git push origin main
# Create branch
git checkout -b feature/new-sensor
# Merge branch
git checkout main
git merge feature/new-sensor
# View history
git log --oneline --graph1550.6.2 Git Workflows for IoT
Feature Branch Workflow:
main (production)
├── develop (integration)
├── feature/wifi-manager
├── feature/mqtt-client
└── bugfix/sensor-calibrationRelease Workflow:
main (v1.0.0)
├── develop (v1.1.0-dev)
├── release/v1.1.0 (preparing release)
└── hotfix/critical-bug (emergency fix for production)1550.6.3 Alternative Version Control
Subversion (SVN): Centralized version control, less common but still used in some organizations.
Mercurial: Distributed VCS alternative to Git.
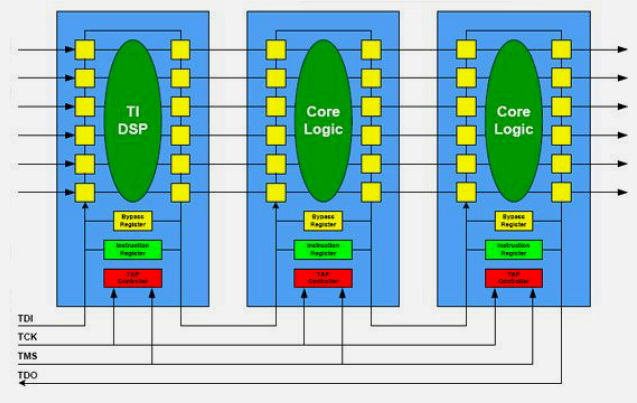
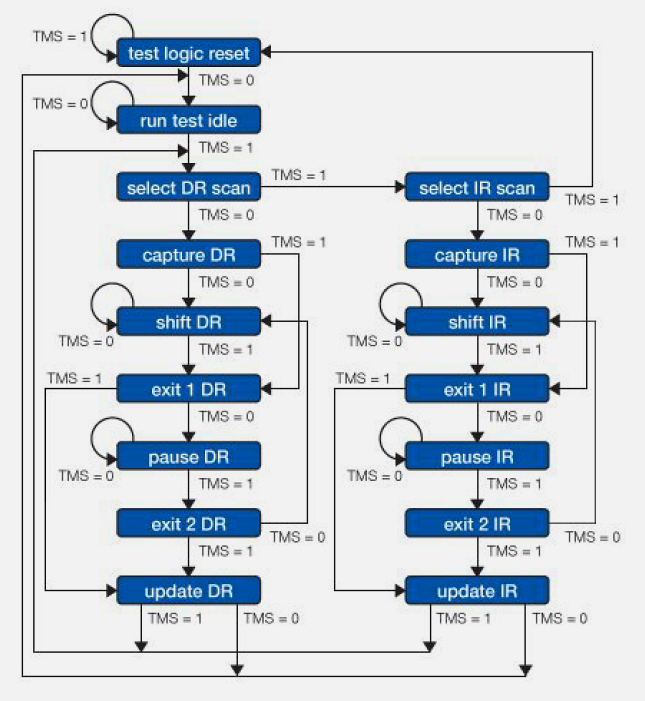
1550.7 Debugging Tools
1550.7.1 Serial Monitor
Basic debugging through UART communication.
Usage:
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("System initializing...");
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Sensor value: ");
Serial.println(readSensor());
delay(1000);
}1550.7.2 GDB (GNU Debugger)
Powerful debugger for embedded systems.
Basic Commands:
# Start GDB with firmware
arm-none-eabi-gdb firmware.elf
# Connect to target
(gdb) target remote localhost:3333
# Set breakpoint
(gdb) break main.cpp:42
# Run program
(gdb) continue
# Step into function
(gdb) step
# Step over function
(gdb) next
# Print variable
(gdb) print temperature
# Watch variable
(gdb) watch sensorValue
# View backtrace
(gdb) backtrace1550.7.4 Logic Analyzers
Capture and analyze digital signals.
Saleae Logic: Popular USB logic analyzer with excellent software.
Features: - Protocol analyzers (I2C, SPI, UART, CAN, etc.) - Trigger conditions - Measurements and timing - Export to CSV
Example Use Cases: - Verify I2C communication timing - Debug SPI protocol issues - Analyze timing between GPIO signals - Capture and decode UART traffic
1550.7.5 Oscilloscopes
Visualize analog and digital signals.
Applications: - Measure signal integrity - Analyze PWM signals - Debug power supply issues - Verify analog sensor outputs
USB vs Benchtop: - USB oscilloscopes: Portable, affordable ($50-500) - Benchtop: Professional features, higher performance ($500-5000+)
1550.7.6 AI-Generated Debugging Visualizations
1550.8 Testing Frameworks
1550.8.1 Unity Test Framework
C testing framework popular in embedded systems.
test_sensor.c:
#include "unity.h"
#include "sensor.h"
void setUp(void) {
initSensor();
}
void tearDown(void) {
// Cleanup
}
void test_sensor_initialization(void) {
TEST_ASSERT_TRUE(isSensorReady());
}
void test_temperature_reading(void) {
float temp = readTemperature();
TEST_ASSERT_FLOAT_WITHIN(0.1, 25.0, temp);
}
void test_temperature_bounds(void) {
float temp = readTemperature();
TEST_ASSERT_TRUE(temp >= -40.0 && temp <= 85.0);
}
int main(void) {
UNITY_BEGIN();
RUN_TEST(test_sensor_initialization);
RUN_TEST(test_temperature_reading);
RUN_TEST(test_temperature_bounds);
return UNITY_END();
}1550.8.2 Google Test (gtest)
C++ testing framework.
test_sensor.cpp:
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
#include "sensor.h"
class SensorTest : public ::testing::Test {
protected:
void SetUp() override {
sensor.init();
}
void TearDown() override {
sensor.shutdown();
}
Sensor sensor;
};
TEST_F(SensorTest, Initialization) {
EXPECT_TRUE(sensor.isReady());
}
TEST_F(SensorTest, TemperatureReading) {
float temp = sensor.readTemperature();
EXPECT_GE(temp, -40.0);
EXPECT_LE(temp, 85.0);
}
TEST_F(SensorTest, MultipleReadings) {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
float temp = sensor.readTemperature();
EXPECT_FALSE(isnan(temp));
}
}1550.8.3 pytest (Python)
Testing framework for Python-based IoT (Raspberry Pi, MicroPython).
test_sensor.py:
import pytest
from sensor import TemperatureSensor
@pytest.fixture
def sensor():
s = TemperatureSensor(pin=4)
yield s
s.cleanup()
def test_initialization(sensor):
assert sensor.is_ready()
def test_temperature_reading(sensor):
temp = sensor.read_temperature()
assert -40.0 <= temp <= 85.0
def test_multiple_readings(sensor):
readings = [sensor.read_temperature() for _ in range(10)]
assert all(-40.0 <= r <= 85.0 for r in readings)1550.8.4 Continuous Integration
Automated testing on code commits.
.github/workflows/iot-tests.yml:
name: IoT Firmware Tests
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup PlatformIO
run: pip install platformio
- name: Run tests
run: pio test
- name: Build firmware
run: pio run1550.9 Documentation Tools
1550.9.1 Doxygen
Documentation generator for C/C++ code.
Example Comments:
/**
* @brief Read temperature from sensor
*
* Reads the current temperature value from the BME280 sensor
* and applies calibration offset.
*
* @return Temperature in Celsius, or NAN if read fails
* @throws SensorException if sensor not initialized
*/
float readTemperature() {
if (!sensorReady) {
return NAN;
}
float raw = bme.readTemperature();
return raw + CALIBRATION_OFFSET;
}1550.9.2 Sphinx
Python documentation generator.
Example (reStructuredText):
def read_temperature():
"""Read temperature from sensor.
Reads the current temperature value from the BME280 sensor
and applies calibration offset.
Returns:
float: Temperature in Celsius
Raises:
SensorException: If sensor not initialized
Example:
>>> sensor = TemperatureSensor()
>>> temp = sensor.read_temperature()
>>> print(f"Temperature: {temp}°C")
"""
pass1550.9.3 README Documentation
Essential project documentation template:
IoT Temperature Monitor README:
- Overview: A battery-powered IoT device monitoring temperature and humidity
- Hardware: ESP32 DevKit, BME280 sensor, 18650 battery
- Dependencies: PlatformIO, Adafruit BME280 Library, PubSubClient (MQTT)
- Configuration: Copy
config.h.templatetoconfig.h, edit Wi-Fi and MQTT credentials - Usage:
pio run --target uploadthenpio device monitor - License: MIT
1550.10 Simulation Tools
1550.10.1 Wokwi
Online Arduino and ESP32 simulator.
Features: - Web-based, no installation - Visual circuit building - Real-time simulation - Code editor with debugging - Library support
Use Cases: - Testing code without hardware - Educational demonstrations - Prototyping circuit designs - Sharing reproducible examples
1550.10.2 Proteus
Professional electronics design and simulation.
Features: - Schematic capture - PCB layout - Microcontroller simulation (PIC, AVR, ARM) - SPICE analog simulation - IoT libraries
1550.10.3 Fritzing
PCB design tool popular in maker community.
Features: - Breadboard view - Schematic view - PCB layout - Parts library - Export Gerber files
1550.10.4 Tinkercad Circuits
Browser-based Arduino simulator.
Features: - Visual programming (blocks) - Text-based coding - Circuit simulation - 3D design integration
1550.11 Collaboration Tools
1550.11.1 Code Hosting Platforms
GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket:
Features: - Version control hosting - Issue tracking - Pull requests / Merge requests - CI/CD integration - Wiki and documentation - Project boards
1550.11.2 Team Communication
Slack/Discord:
IoT Integration: - Webhook notifications (build status, deployments) - Bot integrations - File sharing - Channel organization
1550.11.3 Project Management
Jira/Trello:
Workflows: - Backlog → In Progress → Testing → Done - Bug tracking and prioritization - Sprint planning - Burndown charts
1550.11.4 Knowledge Sharing
Confluence/Notion:
Content: - Architecture documentation - API specifications - Deployment guides - Troubleshooting guides
1550.12 Summary
- IDEs and Editors range from beginner-friendly Arduino IDE to professional VS Code with PlatformIO and CLion for advanced C++ development
- Build Systems (Make, CMake, PlatformIO) automate compilation, linking, and deployment with reproducible configurations
- Version Control with Git enables team collaboration through feature branches, pull requests, and code review workflows
- Debugging Tools span from simple serial monitor output to sophisticated JTAG hardware debuggers with breakpoints and memory inspection
- Testing Frameworks (Unity, Google Test, pytest) enable automated verification at unit, integration, and system levels
- Documentation Tools (Doxygen, Sphinx) generate API references from code comments
- Simulation Tools (Wokwi, Proteus, Tinkercad) enable testing without physical hardware
- Collaboration Tools (GitHub, Slack, Jira) facilitate team communication and project management
1550.13 What’s Next
The next chapter covers Best Practices, which provides guidelines for selecting the right tools and paradigms for your IoT projects, along with knowledge checks to test your understanding.
Continue Learning: - Programming Paradigms - Programming approaches - Best Practices - Tool selection guidelines - Code Examples - Complete practical implementations
Software Development: - Software Platforms - Frameworks - Simulating Hardware - Simulation tools
Hardware Integration: - Prototyping Hardware - Hardware platforms - Specialized Kits - Development kits
Learning Hubs: - Simulations - Interactive tools
