%%{init: {'theme': 'base', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#2C3E50', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#16A085', 'lineColor': '#16A085', 'secondaryColor': '#E67E22', 'tertiaryColor': '#fff'}}}%%
flowchart LR
A[1. Duty Cycling<br/>Fundamentals] --> B[2. ACE System<br/>& Shared Context]
B --> C[3. Code Offloading<br/>& Heterogeneous]
C --> D[4. Optimization<br/>& Assessment]
style A fill:#16A085,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style B fill:#27AE60,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style C fill:#E67E22,stroke:#2C3E50,color:#fff
style D fill:#2C3E50,stroke:#16A085,color:#fff
1608 Context-Aware Energy Management
1608.1 Context-Aware Energy Management
This section provides a stable anchor for cross-references to context-aware energy management across the book.
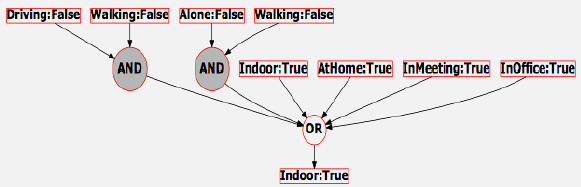
Context-aware energy management enables IoT devices to dynamically adapt their operation based on real-time understanding of user behavior, environmental conditions, and system state. Rather than using static power budgets, context-aware systems optimize for each specific situation, achieving energy savings of 60-80% while maintaining user experience.
1608.2 Chapter Overview
This topic has been organized into four focused chapters for easier learning:
1608.2.1 1. Duty Cycling Fundamentals
Learn the foundation of low-power IoT design through duty cycling - the practice of periodically waking devices for sensing and returning to sleep mode.
Key Topics: - Duty cycle calculation and average power - Interactive duty cycle calculator - Deep sleep vs light sleep modes - Fixed vs event-driven wake-up strategies - Common misconceptions about duty cycling
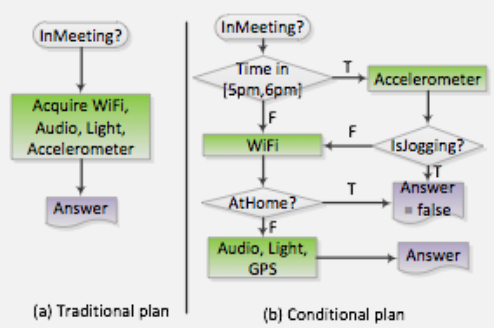
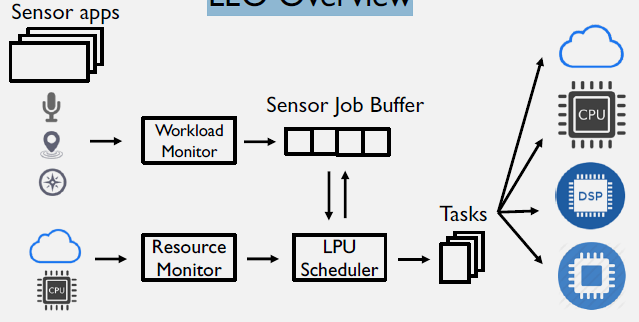
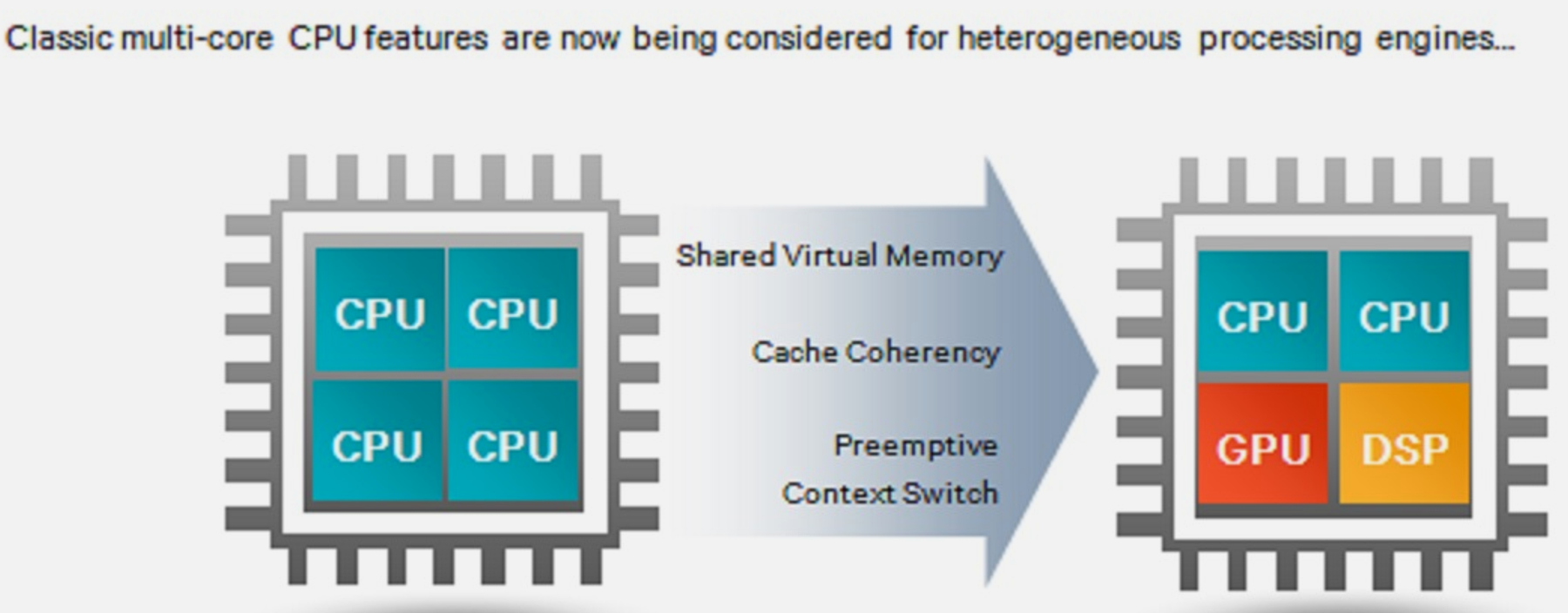
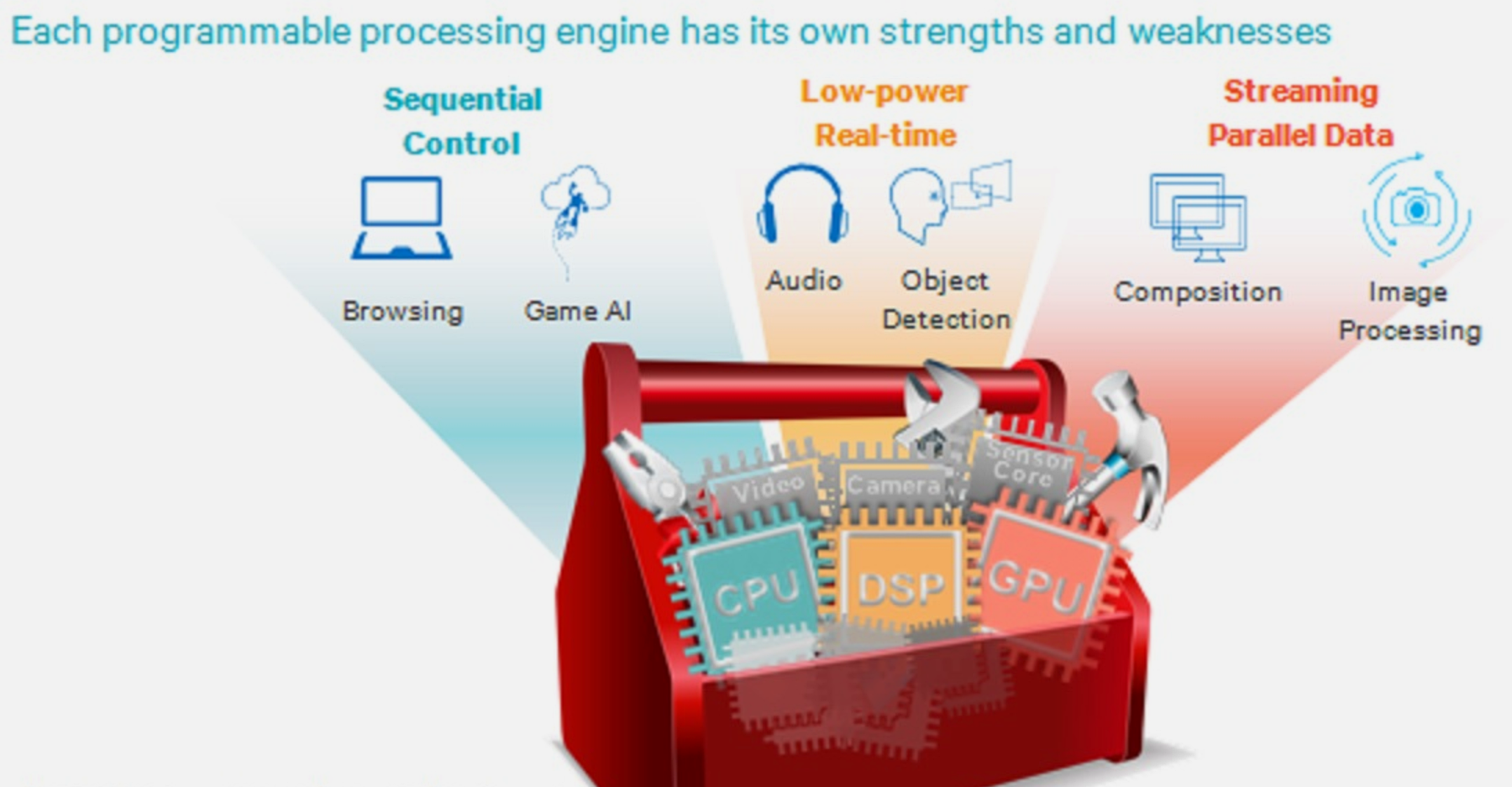
1608.2.3 3. Code Offloading and Heterogeneous Computing
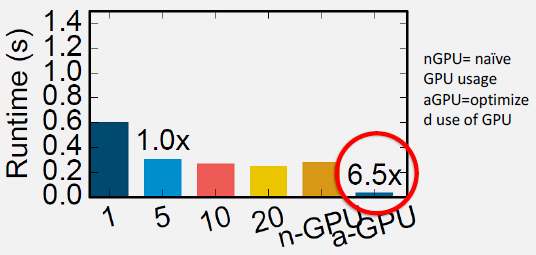
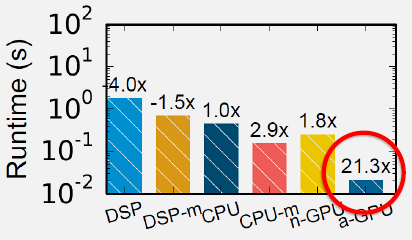
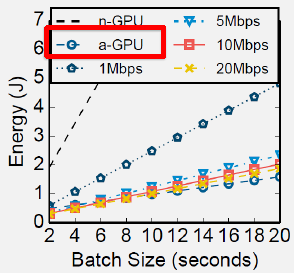
Understand when to process locally versus offload to cloud, and how to leverage heterogeneous processors (CPU, GPU, DSP, NPU) for energy-efficient execution.
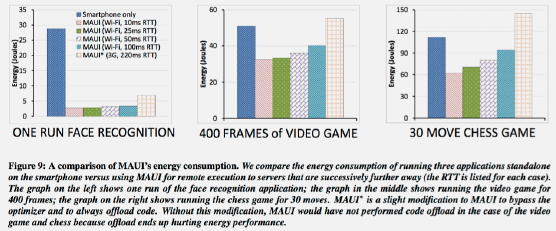
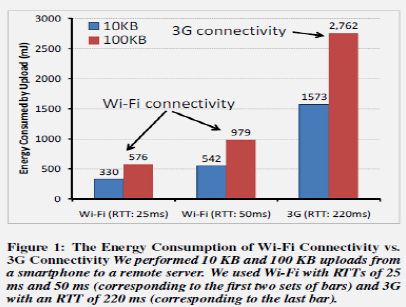
Key Topics: - Energy-preserving sensing plans - MAUI offloading framework - Wi-Fi vs cellular offloading trade-offs - Heterogeneous core scheduling - Code offloading worksheets
1608.2.4 4. Energy Optimization Worksheets and Assessment
Apply your knowledge through comprehensive worksheets, quizzes, and practical exercises covering all aspects of context-aware energy management.
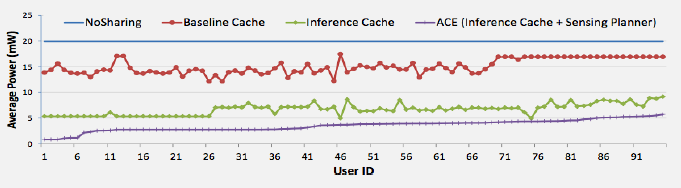
Key Topics: - Context-aware battery life calculations - Mixed usage analysis - ACE system energy savings calculations - Comprehensive assessment questions - Key concepts reference
1608.3 Learning Path
For the best learning experience, work through these chapters in order:
1608.4 Quick Reference: Key Figures
The following figures are distributed across the chapters:
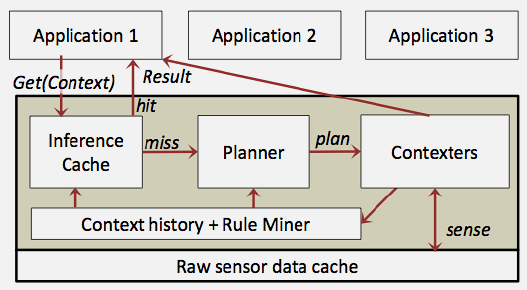
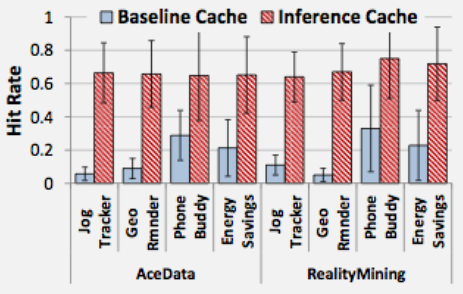
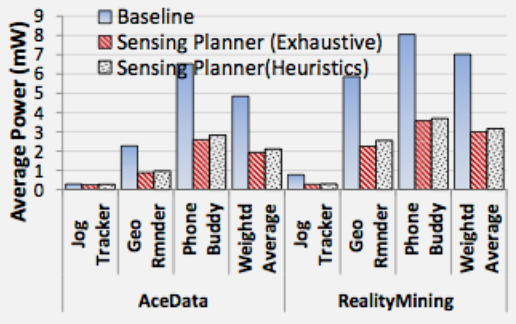
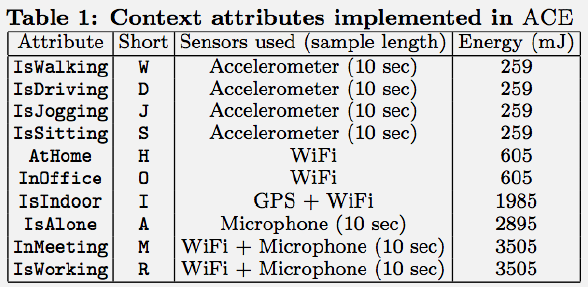


1608.6 What’s Next
Start with Duty Cycling Fundamentals to learn the foundation of low-power IoT design, or jump to any specific chapter based on your learning needs.
